The creation of the state of Israel in 1948 had large destabilizing effects in the region. Many wars followed between Israel and the Arab nations in the area, but overtime Israel was able to come to peace with some of the nations such as Jordan, Egypt, and many more. However, one country, Iran, was never able to make amends with the state of Israel and tension is still present.
The two nations are separated by Jordan and Syria, leaving the two nations relatively close. The proximity of these two nations has allowed for the countries to be involved in many armed conflicts and proxy conflicts. These conflicts have been ongoing for four decades and have mainly involved Iranian backed terrorist organizations, Hamas and Hezbollah. “By 2019, Iran’s proxies increasingly acted like a network spread across the Middle East in ways that boosted Tehran’s influence and threatened Israel’s security.” (Nada)
Historically, much of the tension between the two nations is relatively recent. The relationship began to decay following the Iranian revolution in 1979. Prior to the revolution the two countries were on fair terms and Israel had a mission set up in Tehran. Hostilities towards the West began once the theocratic regime led by Ayatollah Khomeini began to target Israel due to its occupation of the holy land. Alongside this, Iran attempted to rally the surrounding nations against Israel on the basis of religious homogeny. (Nada)
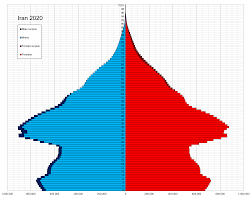
Based on religious demographics the two countries are near opposites. Iran, is 99.4% Muslim according while religious minorities such as Christians, Zoroastrians, Bahai’s, Yarsanis, and Sabean-Mandeans. All of these groups constitute less than 1% of the population with Bahai’s being the largest of the religious minorities in Iran (2020 Report). Currently the total population of Iran sits at eighty six million (Iran Population). The official language of Iran is Persian.
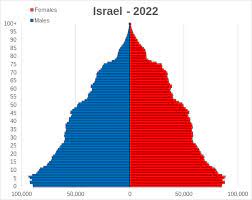
Israel is more religiously diverse, but it is a predominately Jewish state as Jews account for 73% of the 8.8 million people. The remaining religious minorities of the population are 18% Muslim, 2% Christian, and 1.6% Druze (Israel, West Bank and Gaza). The countries official language is modern Hebrew. Population wise, Iran is approximately ten times larger.
The countries also have very different systems of government. The Iranian system of government is a unique one as it is a “unitary Islamic republic with one legislative house. The country’s 1979 constitution put into place a mixed system of government, in which the executive, parliament, and judiciary are overseen by several bodies dominated by the clergy.” Alternatively, the state of Israel is set up as democratic parliamentary system. Israels main lawmaking body, the Knesset, is comprised of a 120 seats (Government of Israel).
Currently, tensions are beginning to flare once again as Iran continues to enrich uranium. Officials in Israel continue to fear the possibility of Iran going nuclear and gaining nuclear weapons. As of now, Israel is the only nuclear power in the region and if Iran were to obtain a nuclear weapon, the balance of power would greatly shift as Iran has openly called for the eradication of the state of Israel . If Iran were to gain a nuclear weapon, the likelihood of war between the states would spike. Israel has already openly spoken about a preemptive strike on the Iranian nuclear facilities and as tensions continue to build, the likelihood of war increases (Ross).
“Age Demographic of Israel.” Wikipedia, https://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=Demographics_of_Israel&oldformat=true#Ethnic_and_religious_groups. Accessed 11 Sept. 2022.
“Age Demographics of Iran.” Wikipedia, https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Demographics_of_Iran. Accessed 11 Sept. 2022.
“Government of Israel.” Encyclopaedia Britannica, Encyclopaedia Britannica, Inc., https://www.britannica.com/place/Israel/Government.
“Iran Population.” Worldometer, https://www.worldometers.info/world-population/iran-population/.
Israel, West Bank and Gaza – United States Department of State. https://www.state.gov/reports/2021-report-on-international-religious-freedom/israel-west-bank-and-gaza/.
“Map of Middle East.” Adobe Stocl, https://stock.adobe.com/images/political-map-of-south-asia-and-middle-east-simple-flat-vector-map-with-yellow-land-and-blue-sea/190109267. Accessed 11 Sept. 2022.
Nada, Garrett. “Iran’s Confrontation with Israel over Four Decades.” The Iran Primer, 19 May 2021, https://iranprimer.usip.org/blog/2020/jan/21/iran%E2%80%99s-confrontation-israel-over-four-decades.
Ross, Dennis. “A New Iran Deal Won’t Prevent an Iranian Bomb.” Foreign Policy, 9 Sept. 2022, https://foreignpolicy.com/2022/09/09/a-new-iran-deal-wont-prevent-an-iranian-bomb/.
2020 Report on International Religious Freedom – United States … https://www.state.gov/reports/2020-report-on-international-religious-freedom/.
2 responses to “Israeli and Iranian Tension”
The population chart is really interesting. I’m wondering why Iran has more of a middle-aged population demographic than Israel.
This was a super fascinating topic to read about. It’s a serious and extremely pressing issue that I thought this article explained really well. The addition of the age demographics was interesting as well, especially Iran’s, for it had that huge population boom at the center.