3D printers are powerful tools for visualization, invention, and creation. In the Media Center, we are pleased to offer you access to these printers, but ask that you please contact a member of the Academic Technology department to learn proper use and ensure we can continue to offer access to 3D printing to all.
1. Saving your Object
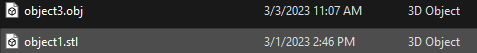
You will want to make sure the object you want to print is saved as an STL, OBJ, X3D or 3MF file type. The file type is listed after the file name as shown below.
2. Preparing your Object for Printing
On the computer located next to the 3D printers in The Makery, sign into the Temp account using the below login information:
User: Temp
Pass: dson1223!
3. Opening the CURA Software
From the desktop, select the green Cura icon.

The software should open a blank project. If it instead loads a previous project, select File > New Project.
4. Importing your file into CURA
In Cura, click on the folder icon in the top left of the screen and select your file. Note: you can select multiple files to import by holding Ctrl on your keyboard, but you will need to properly arrange the objects on the platter prior to printing (see step 6).

5. Placing Objects on the Build Plate
The build plate is the grid under the object that defines the area that the printer is capable of printing within.
To create a 3D object, the printer stacks layers from the bottom up which means that each layer must be supported. This usually involves placing the large, flat side of the object onto the build plate.
For example, if printed the table in the below image, you would want to flip the table onto it’s surface to ensure there is ample support for the print.
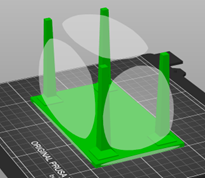
To rotate the object to the face that’s on the build plate:
- Select the object.
- Click the “Rotate” button in the left-hand menu.
- Use the red, green, and blue wheels to rotate the object to the desired orientation for printing.
- Click the Lay Flat button located beside the rotate button to ensure the desired face will be placed directly onto the build plate.
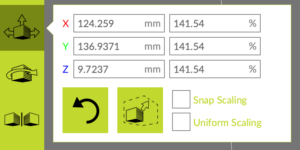
6. Manipulating your Object
The menu on the sidebar displays the types of manipulations you can perform.
- Rotate the camera. Hold the Control Key and click and drag anywhere in the window.
- Move an object. With the object selected, click the icon of the box with a single large arrow. Then, drag the arrow in the direction that you want the object to move.

- Scale an object. With the object selected, click the icon with three arrows and a box. Scale the object by dragging any of the small boxes that have appeared around the object.

- Rotate an object. With the object selected, click the icon with the curved arrow. Drag each square in the direction you would like to rotate the object.

- Precise control. Use the object manipulation values that appear in the menus beside each of the above icons when selected.
7. Resetting Printer Settings
Before printing an object, the printer settings should be set to default.
Be sure that the “Profile” option on the right-hand side of the screen is set to “Standard” or “Highspeed” (other profiles don’t add much benefit and are time consuming):

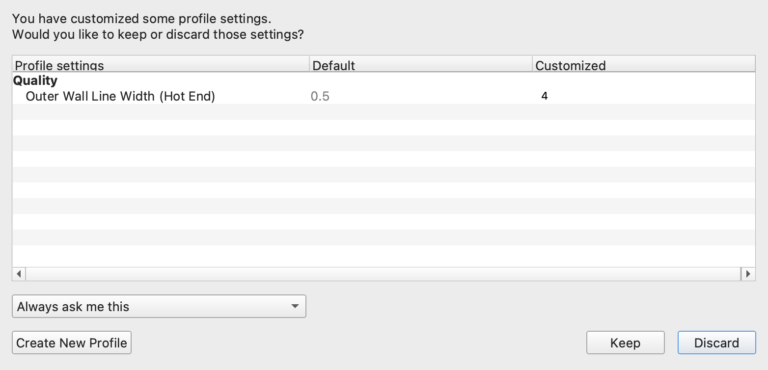
Then, ensure that no star appears next to the selected profile. The star symbol, depicted below, indicates modifications have been made to the profile.

If the star symbol appears next to the selected profile:
- Click the “Profile” dropdown and re-select the profile you want to use.
- A message will appear asking if you would like to “Discard or Keep Changes”. Click Discard. The star should disappear.
8. Deciding on Supports
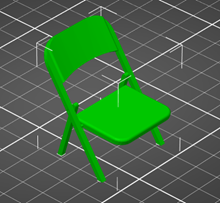
If a part of your model exists without support directly beneath it, it needs supports. For example, the chair seen in the below screenshot cannot be rotated in an orientation where every piece is supported from below. In other words, it needs supports.
Although some prints can be rotated to avoid using supports (see the screenshot in step 5), oftentimes, you will need to add supports. To do so, check the box next to Generate Support in the right side of the Print Settings menu.

Supports can be pulled away once the print is finished.
Note: even if using supports, the object should still be placed in an orientation that minimizes the amount of supports needed for the object (see step 5).
9. Determining the Infill
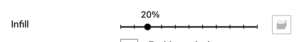
Infill provides support from inside the object. Most objects should have between a 5% and 15% infill. The more infill you add, the stronger your print will be and the longer it will take to print.
To change the infill, adjust the Infill slider located on the right side of Print Setup menu.
10. Selecting the Material
Please don’t adjust the “Material” dropdown” menu. If you want to change the 3D printer material, please ask a Media Center employee.

11. Preparing for the Printer
In the Cura software, click the Monitor tab at the top of the screen.

Click Connect and wait until the “USB Printing, Connected Via USB” message is displayed at the top. Note: You may have to try connecting a couple of times before this message is displayed.

12. Starting your Print
In the Cura software, click the “Start Print” button at the bottom right.

The printer will heat up and begin its calibration process.
Once it’s ready, it will begin printing. Please wait at the printer to ensure your object actually begins printing. If your print does not start, ask a Media Center employee for help.
13. Removing your Object from the Build Plate
Peel up the build plate from the printer. Remove your object by gently bending the build plate and pulling the object off the surface. If it’s stuck, you may have to use something to carefully scrape it off the surface, paying extra attention to not damage the plate.
Remember to remove any and all filament from the print surface so that the plate is completely clean before being placed back onto the printer.
If you used supports, you may have to use pliers to carefully remove them from your print.
