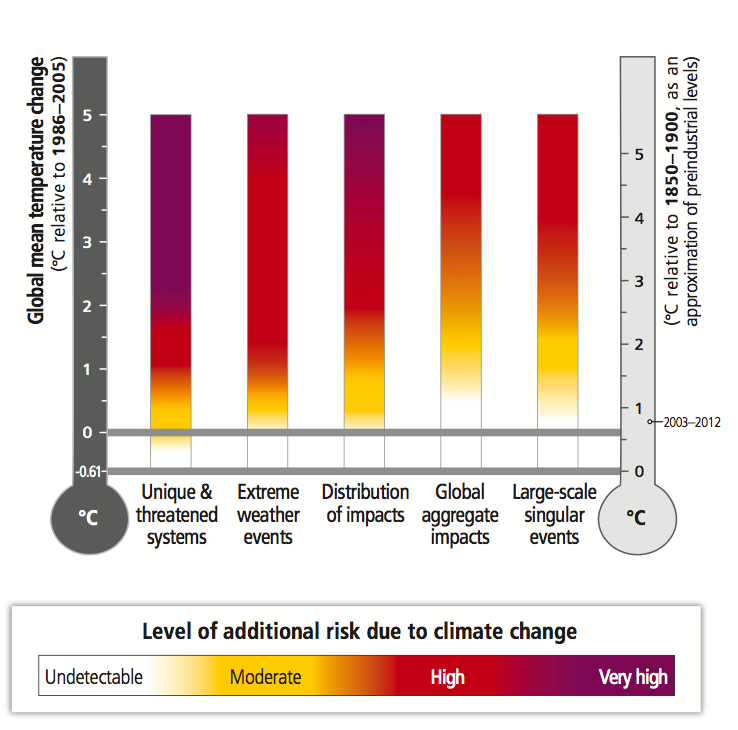
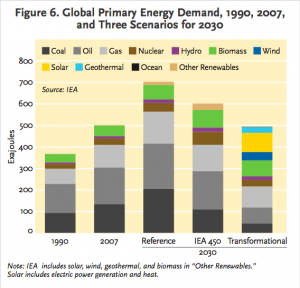
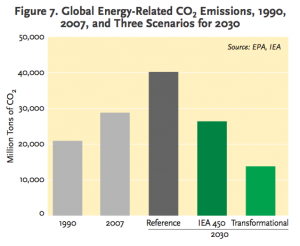
Climate change mitigation can work hand in hand with development. In fact, a “green” world currently seems like the best economic option. According to a study by MIT, certain policies to decrease carbon emissions would save large amounts of money if implemented, even without calculating in the benefits from mitigated climate change (Resutek 2014). Lessening future climate change is not a cost to disregard either; refusing to take drastic measures to mitigate climate change only creates increased costs the future. According to a new report from the White House, allowing the climate to warm 3ºC would decrease global productivity by 0.9 percent. 0.9 percent of the United States’ GDP alone is over $150 billion (House 2014). All around the world, communities are transitioning to infrastructure that is run by renewables (Sawin and Moomaw 2009). These communities must be used as models and frame a new, low-carbon infrastructure system for the globe. A low-carbon world is needed urgently and working towards this world will increase development and decrease premature deaths.
There is a cost in transitioning to a less carbon intensive world, but there is an even greater economic benefit. Establishing a cap-and-trade policy on carbon will create over 10.5 times the benefit in health benefits alone than the cost of the policy (Resutek 2014). This is only a small portion of the total benefits that will accompany a low carbon world. Furthermore, costs from reduced use of fossil fuels and improved technology methods are less of a moral “cost” than the costs of asthma and other illnesses. We must work together to create a healthier, cleaner world.
By increasing the energy efficiency of households and infrastructure and convert to renewable fuels, we can raise the standard of living for many people while also decreasing the odds of experiencing catastrophic climate change. As the Worldwatch report states, “the current reliance on fossil fuels is not supportable by poor developing countries, and increasing demand for fossil fuels is creating dangerous competition for remaining available resources of oil and gas” (Sawin and Moomaw 2009, 6). Renewables such as solar can allow people in less developed places to use clean energy without being on a grid or contributing to poor air quality and climate change. Competing for the last amount of oil will only result in war and high amounts of climate change. It is much smarter to forget the stored carbon and move on together with new technology.
These shifts can and are happening quickly. Germany had virtually no renewable energy industry in 1990 but is now a world leader in solar and wind. This seemingly cloudy country has increased solar photovoltaics by a factor of more than a hundred. Denmark, Sweden, China, Brazil and Israel are quickly transitioning their energy sector. For the first time, in 2008, investment in new renewable power capacity exceeded that for fossil-fueled technologies. Revamping the energy system of communities creates new industries and jobs. In Gussing, Austria, the community members used biodiesel to become energy self-sufficient and improved the quality of life for the local residents (Sawin and Moomaw 2009). Working within and among communities can be a powerful tool for combating climate change while improving standards of living for world citizens.
The Worldwatch report creates a scenario of the United States transitioning to a renewable energy economy; however, an actual application of this idea does not currently seem politically feasible. The scenario can be achieved by first increasing energy efficiency of all states, requiring all new buildings to be zero-carbon and retrofitting two-thirds of currently existing buildings, reducing heat waste in industries, and shifting towards a reliance on renewable energies. The report, produced in 2009, says that a “green” U.S. can emerge by 2030 (Sawin and Moomaw 2009). The pictures of clean energy for everyone, improving the lives of the impoverished, using the most efficient economic policy to produce mass health and climate benefits, or transitioning entire economies to efficient renewables seems almost unfeasible at the moment. In reality, if we start towards these goals, the policy will be much messier and less economically efficient. Transitioning will take much longer than could be possible. Providing development aid to poorer countries may be much less than needed. A perfect scenario to slow climate change should not be expected. Moving forward to a “green” world does not necessarily need to be a straight line, but as long as we keep fighting for change, some good will happen.
References
White House. June 2014. The Cost of Delaying Action to Stem Climate Change. Executive Office of the President of the United States.
Resutek, Audrey. 2014. Study: Cutting emissions pays for itself. August 24. http://newsoffice.mit.edu/2014/cutting-carbon-health-care-savings-0824.
Sawin, Janet L., and William R. Moomaw. 2009. Renewable Revolution: Low-Carbon Energy by 2030. Worldwatch Institute.