Healthcare institutions have many concerns to navigate, however in modern society cybersecurity is the most prominent.
There has been a rise in cybersecurity breaches given the advances in technology and this has put hospitals and patients’ privacy and safety at risk.
Additionally, there a lot of financial and operation risks that coincide with online security breaches. A recent study discusses the major risks and players in cybersecurity to aide healthcare professionals and policymakers to make proper protocol decisions and precautions to ensure better safety regarding cyber protection to the hospital, the staff and the patients.
There are four major players in cybersecurity, end users, cyber defenders, developers and cyber-attackers. End users can both threaten or defend cybersecurity. Malicious end users are considered insiders and are extremely dangerous because of their knowledge of the system, its strengths and weaknesses. Non-malicious end users is a bit of a complicated name because the person themselves are not intentionally harming, but someone else is using their information or machine as a host to attack a security from there. An example would be spam emails that carry an attack and the person that opens it is the non-malicious end user.

Image retrieved from Flickr.
Cyber defenders are individuals that work to protect software from cyberattacks and ensure security. Most of the time IT professionals or government employees fall into this category. Developers are essentially the most important part, they are the ones that create the software and have to ensure there are no weaknesses or mistakes that cyber attackers can take advantage of. Unfortunately, this is very difficult and malware can easily be introduced to a system when there are mistakes, thus the developer is the first line of defence. When they fail, cyber-attacks are inevitable.
Cyberattacks are the main security threat to a network or software’s’ security. There are five main categories within cyberattacks; denial of services (DoS), privilege escalation, man in the middle (MITM), cryptographic attack and malicious software. A DoS attack overloads a network with information and the purpose is to disrupt service or temporarily shut down the network. Issues of this attack for healthcare is that it can prevent workers from accessing or sending essential information during the attack, which can become very dangerous for patients depending on their condition. Privilege escalation uses weaknesses in the system to manipulate for the sole purpose of gaining a higher level of access to the program or network in question. This becomes problematic in healthcare because the access can allow a hacker to change information such as a patient’s information, which results in a massive invasion of privacy as well as endangering the patients’ safety. MITM is a cyberattack technique that essentially eavesdrops on the network. They appear to be a middle man, communicating between two parties, but this is extremely
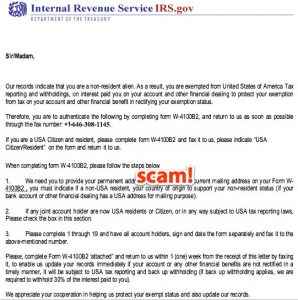
An example of a scam email that some malicious software can use. Image obtained from Flickr.
dangerous because they can change the information being transferred between people without anyone knowing. In some situations, this form of cyberattack as also been used to blackmail patients or healthcare workers, which is evidently problematic. A cryptographic attack is gaining access to information and decrypting it to reveal information to the public, posing as a huge issue to privacy and confidentiality. Lastly, malicious software is a form of cyberattacking that attacks a system and compromises it without needing permission from the user. About 90% of cyberattacks are from malicious software because it can alter, spy or delete any information on the system, putting patients, workers and hospitals at risk.
In general cybersecurity is at a huge risk in the modern age given all thetechnological advances we have. However, the technology also offers helpful ways to counteract the attacks and ensure security. This study was created for healthcare organizations, because cybersecurity will greatly influence the success of hospitals. The policy and management suggestions given in this study ensure proper prevention and protocol to limit cyberattack occurrence as much as possible. These suggestions consist of the best developers and healthcare systems to use, like Medicare or Medicaid. As well, they give advice for healthcare administrators to ensure they teach proper protocol to their staff, which will eliminate at least half if not more of the cyberattack threats when everyone knows what to look for, such as in scam or “phishing” emails. Overall, this study is very helpful for hospitals and healthcare organizations to provide them more knowledge and suggestions for protecting cybersecurity, subsequently protecting the hospitals, workers and patients.
Source:
Bhuyan, S., Kabir, U., Escareno, J., Ector, K., Palakodeti, S., & Wyant, D. et al. (2020). Transforming Healthcare Cybersecurity from Reactive to Proactive: Current Status and Future Recommendations. Journal Of Medical Systems, 44(5). doi: 10.1007/s10916-019-1507-y

Alex
"This title was very eye catching! That is so interesting that such a ..."
Alex
"This is really interesting! The fact that crops and plants are damaged is ..."
Alex
"Well done, this article is great and the information is very captivating! Ethics ..."
Alex
"I was intrigued throughout the whole article! This is such an interesting topic, ..."
Alex
"This is such an interesting article, and very relevant!! Great job at explaining ..."
Grandpa
"Honey You Did a good job I will forward to my eye doctor "
murphymv
"This article is fascinating because it delves into the details of the research ..."
murphymv
"I agree, adding the photo helped solidify the main finding. "
murphymv
"This is a fascinating finding. I hope this innovative approach to improving transplants ..."
Sherzilla
"This is a great article! I would really love to hear how exactly ..."
Sherzilla
"It's disappointment that these treatments were not very effective but hopefully other researchers ..."
Sherzilla
"I agree with your idea that we need to shift our focus to ..."
Sherzilla
"It's amazing to see how such an everyday household product such as ..."
Lauren Kageler
"I will be interested to see what the data looks like from the ..."
Lauren Kageler
"A very interesting article that emphasizes one of the many benefits that the ..."
maricha
"Great post! I had known about the plight of Little Browns, but I ..."
Sherzilla
"I assumed cancer patients were more at risk to the virus but I ..."
Sherzilla
"Great article! It sheds light on a topic that everyone is curious about. ..."
maricha
"This article is full of really important and relevant information! I really liked ..."
maricha
"Definitely a very newsworthy article! Nice job explaining the structure of the virus ..."
maricha
"It's interesting to think that humans aren't only species dealing with the global ..."
murphymv
"This is very interesting and well explained. I am not too familiar with ..."
Lauren Kageler
"Great article! This post is sure to be a useful resource for any ..."
Lauren Kageler
"Definitely seems like an odd pairing at first, but any step forward in ..."
murphymv
"What an interesting article! As you say, height and dementia seem unrelated at ..."
murphymv
"Great article! I learned several new methods of wildlife tracking. This seems like ..."
murphymv
"Very interesting topic! You explained cascade testing and its importance very well. I ..."
Alex
"This article is really interesting! What got me hooked right away was the ..."
Sabrina
"I found this article super interesting! It’s crazy how everyday products can cause ..."
Erin Heeschen
"I love the layout of this article; it's very eyecatching! The advancements of prosthetics ..."
murphymv
"Awesome article! I like the personality in the writing. Flash Graphene not only ..."
murphymv
"Very interesting work! I don't know a whole lot about genetics, but this ..."
Cami Meckley
"I think the idea of using virtual reality technology to better help prepare ..."
Erin Heeschen
"I wonder if there's a connection between tourist season and wildfires in the ..."
Ralph berezan
"Not bad Good work "
Michelle
"This sounds like it would be a great tool for medical students! ..."