Earlier this week, famed nature photographer and documentarian James Balog was on Dickinson’s campus for a two-day residency as part of the Rose-Walters Prize he received at Commencement this past May. His vivid pictures and time-lapse videos of glacial retreat are a stark representation of the scope and rate of global warming and climate change in our own lifetime. While Balog approached his photography as an avenue for showing the beautiful destruction of the climate, Brazilian photographer Sebastião Salgado’s most recent work, Genesis, shows the inherent beauty of the world that is at peril of being disturbed or lost forever to the effects of climate change. Deserts, ice, endangered species, beautiful designs naturally cut along a valley are a few of the subjects of Salgado’s photographs. His work approaches the same vein as Balog’s, just from a different angle, and both angles have a story that is important for everyone to experience and internalize as we approach the climate question. The Earth around us is a beautiful, one-of-a-kind environment that is imperative for us to cherish and protect from ourselves so that future generations may have the privilege and honor to cherish and protect it as well. As we move forward in our work this semester at COP20 and in all future climate negotiations, it is crucial that this message not be lost upon us.
Actors pretend for a living, the rest of the population does not.
Tuesday morning actor Leonardo DiCaprio addressed world leaders at the UN Climate Summit. What was this product of hollywood doing in a room full of heads of states? Well, he compared his acting career of “pretending for a living” and “solving fictitious problems” to how humankind is confronting climate change, pretending it is not happening to our planet. I’m sure many of us has seen hollywood “climate-fiction” films such as The Day After Tomorrow, but we must be able to differentiate fact from hollywood’s fiction. Is getting the fictitious world of hollywood involved in the fight against climate change an effective wake up call? How do we get the people to stop pretending and face reality?
Read DiCaprio’s full speech here
Exploitation At It’s Finest

Exploitation At It’s Finest
One idea in the passage that does not allow for interpretation is that humankind is exploiting the world for its resources that help us survive, but this exploitation of earth for our needs is coming to an end with global climate change negotiations and adaptations on the rise. Another widely understood component is that climate change has already struck and is striking currently. In addition, the Parties should be preparing for what has yet to come by reducing the triggers of climate change and by cleaning up the damaging effects that it has already caused.
While there are grave and irreparable damages that climate change has and could cause, it is not the reason to stop trying to bring it to a halt. Even the uncertainty of scientific evidence is not a good enough reason. Earth as we know it will soon disappear because of our doings. We are the reason for it being in this state. One just wonders just how the should go about reducing or stopping the effects of climate change. We want to reduce or stop it where we will benefit the most but at the lowest possible cost. Just how will we do it though?
Global benefits are spoken about in the article. However, there is a question of who will ultimately benefit. Will it be the developed or developing nations? Developed nations carry more CO2 emission weight but developing nations carry some too. Developed nations are more powerful though, which may play a role on who benefits more ultimately. Also, there are implications in figuring out a solution to this problem in a cost effective way. Who will figure that out and how will they figure that out? It is still very vague and up in the air. Cost effectiveness is a factor that drives the solution but it’s not the solution as a whole.

The World May Not Be Flat, But It’s Sure Growing.
Last Thursday, a group of international researchers released a report that projects a global population increase from seven billion today to eleven billion by the end of the century. This overturns a general agreement worldwide that population would only peak at about nine billion people in 2050, which was the assumption underlying a plethora of key scientific reports on malnutrition, HIV/AIDS, demographic composition of different countries, and, most interestingly for our purposes, all previous Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) reports on the threats of climate change and global warming.
This burgeoning population could reach, as Simon Ross from the think tank Population Matters told the Guardian, “between 40-75% larger than today in the lifetime of many of today’s children and will still be growing.” The implications of this on resource use and energy demand will be quite significant: more people will require more resources in order to survive, but the resources are in finite supply, so competition will increase, thus putting pressure on those at the margins who may be denied access. With this grim prospect, we can expect to see more exaggerated poverty and strife worldwide, while aggregate resource use can be expected to increase.
This will pose a large roadblock for any future agreements to reduce greenhouse gas emissions because not only is the necessity for emissions reductions compounding over time, but so is the difficulty of achieving that aim (mainly due to the reasons I discussed above). The momentum must be continued now and aggressive reductions must be made now so that, moving forward, the work before us will be within our reach to achieve; if we wait any longer, that work will only get harder and harder, and further and further out of our ability to cope.
Carrington, Damian. 2014. “World population to hit 11bn in 2100 – with 70% chance of continuous rise.” The Guardian, September 18.
Climate Change and Indigenous Communities in the Arctic
The Arctic, defined as the area north of 66 degrees 33 minutes North latitude, a.k.a. the Arctic Circle, is home to a multitude of indigenous people, among them the Inuit in Greenland, Canada and Alaska, the Inuvialuit in western Canada, the Athabaskan in Alaska and Canada, and the Saami in Norway, Sweden, Finland and northwest Russia. These people’s cultures and traditional lifestyles are shaped by the Arctic environment, and because of this these people are very vulnerable to climate change. For people who depend on a stable local environment to support and sustain their settlements and lifestyle, a changing climate can have a very injurious effect. One of the ways in which the warming climate can adversely affect indigenous people is that the weather becomes less stable and therefore harder to predict. Experienced hunters and elders have reported that traditional techniques of predicting the weather are becoming ineffective, with storms occurring without warning and wind direction changing suddenly. This unpredictability in the weather can present problems when trying to figure out the best times to, say, dry fish, or lead a hunting party. Yet another problem is that the changing climate has brought about more freezing rain. This affects snow characteristics, and nowadays, Arctic natives report that there is a lack of good snow that can be used to build igloos. This is causing an increase in injuries and deaths for members of hunting parties because the hunters are unable to build shelters quickly enough when faced with a sudden storm. Another problem caused by freezing rain is that much of the wildlife of the Arctic, including reindeer and musk ox, cannot find food in the winter due to the thick layer of ice covering these animals’ usual food sources. This will in turn affect the indigenous people who depend on these animals for food. Climate change has also caused sea ice to decline in both extent and thickness. With less sea ice, seas are stormier and more violent, which is dangerous for hunters, as the thin sea ice is very unsafe for travel This also adversely affects anyone else who wants to use the sea ice for transportation, either walking or using sleds. Animals, such as walrus and polar bears, are beginning to see the range of their habitats decreasing, threatening their populations and adding stress to those people who depend on the animals for food and for the warmth that their pelts provide. The indigenous people living above the Arctic Circle depend on a stable environment and stable weather conditions to support their lifestyles, but climate change is causing the landscape of the Arctic to change. Sea ice is less stable, weather conditions are unpredictable, and even the surface of the ground is changing. This is affecting the food supply of these indigenous Arctic people, along with their travel and safety. Although the indigenous peoples of the Arctic might seem as far removed from our society as one can get, we cannot ignore their concerns and troubles, as it is almost a foreshadowing of what might happen to us if we ignore climate change for long enough. Thanks to Neil Leary for the link to the Arctic Climate Impact Assessment: ACIA, Impacts of a Warming Arctic: Arctic Climate Impact Assessment. Cambridge University Press, 2004.

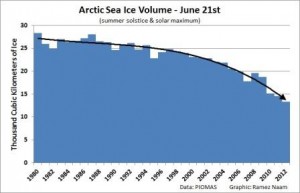




The Weather in 2050
On the UNFCCC newsroom homepage today I found the video at the bottom of this blog post. The first four minutes of the video show a news anchor man going through the current weather across the US with a hurricane off the coast of Florida, a heat wave in Chicago and a server drought in the south-west US. The video ends with Ban Ki-Moon addressing the viewers and asking for us to take action on climate change with him. On one hand the video seems overly dramatic. But, is this what it takes to get people to take up Ban Ki-Moon’s call for action?
After investigating the WMO’s website, I was able to find a link to a series of videos that the organization is running in preparation for the Climate Summit at the end of the month in New York City. A list of those videos can be found here.
It is very interesting to me that they are running this campaign on weather related events. We know that there is not a clear connection between any given daily weather event and climate, yet, this video series suggests that weather when examined in different locations globally is an indication of a warming climate. These videos are consistent with the predictions of climate modelers, according to the WMO website. So, maybe this is an effective way of convincing people of the real dangers of climate change. What do you think?
El Niño and the Peruvian Fishing Industry
The Pacific coast of Peru: one of the world’s richest fisheries. Because the southeast trade winds blow parallel to the coastline in this area, the Coriolis effect and the Ekman transport system deflect surface water to the left of the wind direction and out to sea. In its place, upwelling brings cold water to the surface. This cold water is rich in nutrients, which attract plankton, and in turn fish, to the area just off the shore of Peru.
This upwelling system results in one of the most productive fishing grounds in the world. Half of the world’s commercial fish come from the coast of Peru, which makes up only .1% of the ocean’s surface area. Since 1960, the weightof the Peruvian anchovy catch has exceeded that of any other fish species in the world. But this productivity is vulnerable to extreme variability and fluctuation due to El Niño, a prolonged warming of Pacific Ocean sea surface temperatures that wreaks havoc on fish populations in the area.
During El Niño, weakening trade winds allow warmer water from the Peru countercurrent to flow east toward Peru. Sometimes the trade winds even reverse direction. The warm water brought in by these trade winds overrides the cold water present off the coast because it is less dense. It is also not as nutrient-rich, resulting in a large percentage of fish either dying off or dispersing further offshore toward deeper water that is more nutrient-rich, putting a huge dent in the Peruvian fishing industry. An El Niño event typically last nine months to two years, happening at irregular intervals of two to seven years.
This reduction of the production and exportation of fish from one of the most productive fisheries in the world has injurious effects around the globe. Both poultry and livestock prices spike worldwide, because the fishmeal that is used to feed poultry and livestock is now more expensive. More locally, in Peru, the catch is reduced and people are put out of work, while fishmeal plants and fishing boats remain idle. Workers need to find a way to support their families during these El Niño episodes, and payments must still be made on loans taken out to buy fishing boats and build fishmeal plants. El Niño has a damaging effect on not just the local economy, but on economies worldwide. It is just another way that climate changes in one area of the world can have very damaging effects worldwide.




The Cost of Flying to Peru- INCORRECT
THE BELOW CALCULATIONS ARE INCORRECT. PLEASE GO TO THIS LINK TO SEE THE CORRECT NUMBERS.
During our first class of the semester, while discussing the coming trip to COP20, Neil asked the mosaic to think about the costs of traveling thousands of miles in order to be a part of high-level climate negotiations. For this part of the semester we will not be riding our bikes down the street for class, we will be flying. Air travel is an extremely carbon intensive way to get around, but our only realistic choice (we could sail?). He asked us to reflect on this and during this reflection to ask ourselves how is the carbon emitted from traveling there worth it?
In order to do this I needed to quantify those emissions. Using EPA values for air travel and the emissions per mile of CO2, N2O, and CH4. I then converted those three values into carbon dioxide equivalent values using an EPA calculator. The results are below in Table 1. If you would like the excel worksheet to use for yourself please comment below with an email address. For simplicity’s sake I used four flights as the entire trip. Some of the mosaic will be traveling elsewhere in South America or not returning to Washington DC after the meeting. The four flights are: Flight 1 from Dulles to Panama City, Flight 2 from Panama City into Lima, Flight 3 from Lima to Panama City, Flight 4 from Panama City to Dulles. While this may not be each member of the mosaics travel plans it is easier to group all of us into one. The results are in Table 2. Each flight assumes a total capacity of 177 passengers and spreads the emissions out, per passenger. This means that, according to the EPA, each passenger would be emitting the same amount of carbon as about 25 pounds of coal would, when burned.

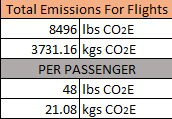

The question I ask myself now is how do I make that worth it? It may not be a huge amount of carbon emitted, but it is still some and I the entire trip will only be resulting in more. This investigation also brought to mind an article in the Wall Street Journal about the coming “People’s Climate March” in NYC. The author points out the amount of emissions that will result in traveling to and from NYC for the marchers. This could be seen as a counterproductive practice, but I think that it is a good point to make. If we treat emissions from travel similar to an investment, can we assume that some sort of positive return will be had? When the mosaic flies to Peru, we have to work as hard as possible to make sure that the cost of our traveling there is not a negative impact on the atmosphere in the long-term, but that it leads to further reductions down the road. Whether that is from the readers of our blog or directly related to something learned from the COP.
An Inconvenient Truth
In 1965, our 36th president Lyndon Johnson delivered a special message to Congress. He said “This generation has altered the composition of the atmosphere on a global scale though…a steady increase in carbon dioxide from the burning of fossil fuels.” These powerful words portrayed how many have known about this issue for a while now. But what has truly been done about it?
Science historians Naomi Oreskes and Erik M. Conway introduce us to this special message in the beginning of the book “Merchants of Doubt: How a Handful of Scientists Obscured the Truth on Issue from Tobacco Smoke to Global Warming.” Throughout the book, you can see how environmental issues have been just swept under the rug because of other pressing issues at hand that needed to be tended to. Newsflash! There will ALWAYS be pressing issues that need to be tended to! How much longer will we keep our lovely planet waiting?
Oreskes and Conway also point out that the media is responsible for how information is represented or should I say… misrepresented. Information is put out in an exciting way by journalists, which is not wrong. That captures people and engages them. However, somewhere along the lines of “exciting” the truth gets lost. Scientists depend on journalists to get it right because they honestly do not have time to deal with public relations. When information is tampered with, it is the public who goes and knocks on doubt’s door, enters and remains there until further information is released. Climate change and media have a very difficult relationship.


Impacts of the Erratic Beast
Coming from a family of Bangladeshi immigrants who want better opportunities for their children and for them to know their roots, my parents made sure my sisters and I knew our culture, language, and traditions. My parents took my sisters and I to Bangladesh at a very young age so we can fully emerge ourselves into our culture.
This past summer I visited Bangladesh for the third time. It was truly a wonderful trip like all of the other times I have visited. However, during this trip I noticed the impacts of climate change; the Erratic Beast. Bangladesh is a beautiful country with so much green scenery but it will soon be gone due to rising sea levels. There was an interesting and thought-provoking film released about the impacts of climate change specifically in Bangladesh called Bangladesh: A Climate Trap. It is a climate trap because of rising sea levels, weather patterns changing, and biological systems being affected with the rise of CO2 levels.
In Spencer R. Weart’s book, “The Discovery of Global Warming”, he address the influences which cause impacts of the Erratic Beast. In 1980, it was found that CO2 played a vital role in climate change. Chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) and nitrates are also influences.
With the melting of ice caps, many countries and islands will soon disappear…








