The Canon VIXIA HF R50 is a compact, easy-to-use camcorder designed for straightforward, reliable video recording. You might choose the VIXIA HF R50 when you need simple setup, long recording times, and dependable video for interviews, presentations, performances, or documentation. It’s well suited for users who want quality video without managing complex camera settings.
This tutorial will help you get started with the Canon VIXIA HF R50 camcorder. Follow the steps below to learn how to power on the camera, record video, and review your footage.
1. Turning the Camcorder On
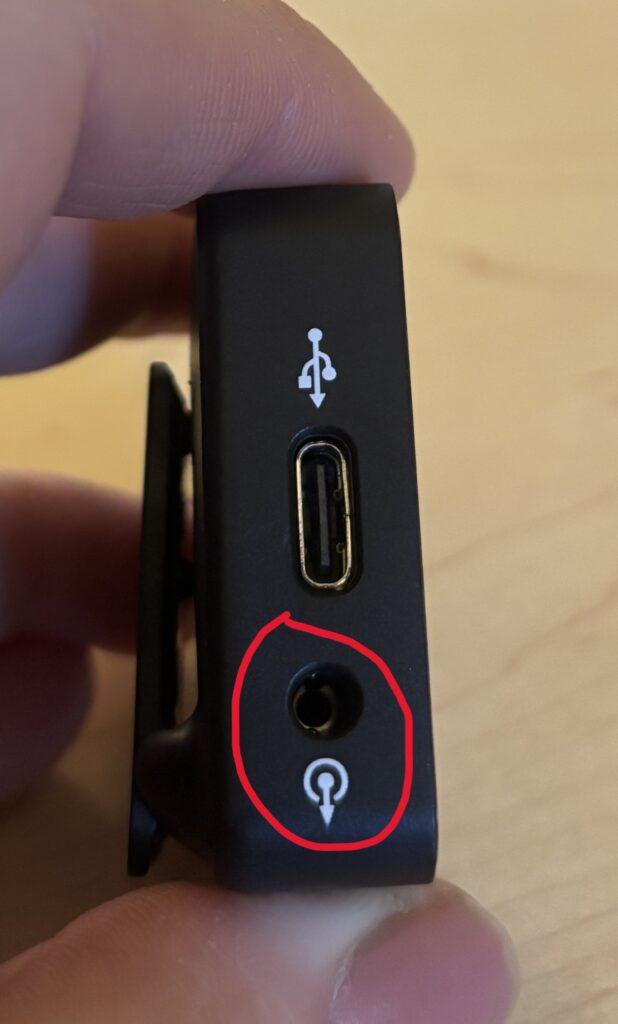
- Make sure the battery is charged and an SD card is inserted
- Press the Power button located on the side of the camera next to the SD card slot
- Flip the switch by the lens to open its cover
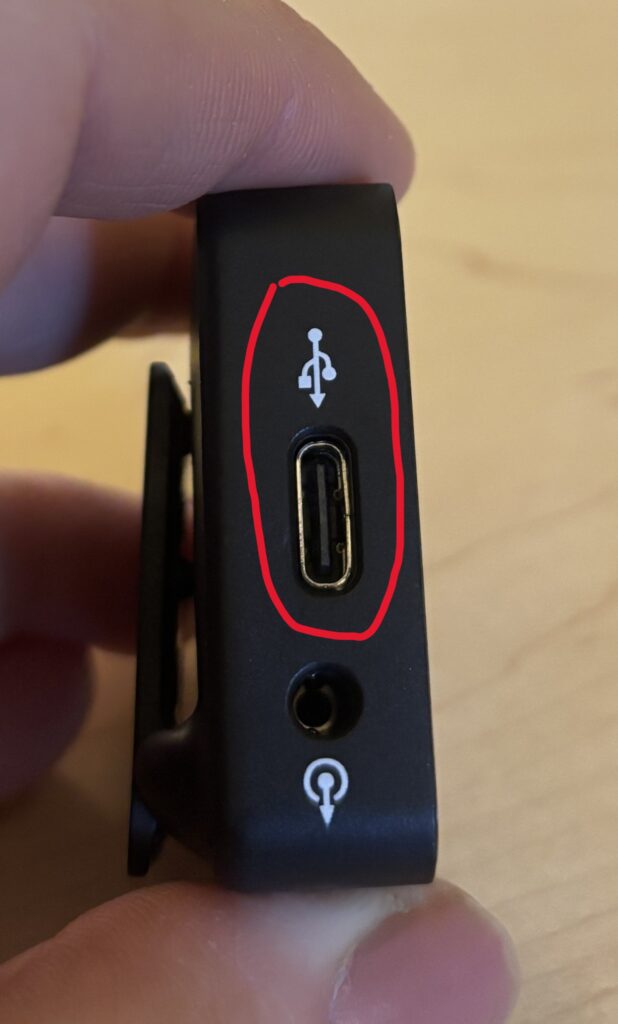
2. Recording to the SD Card
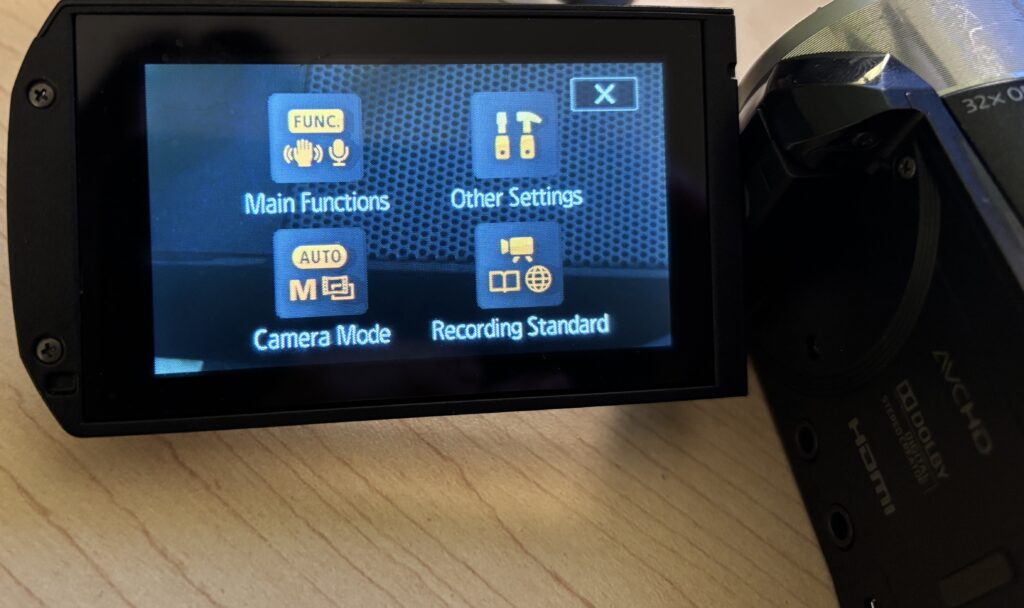
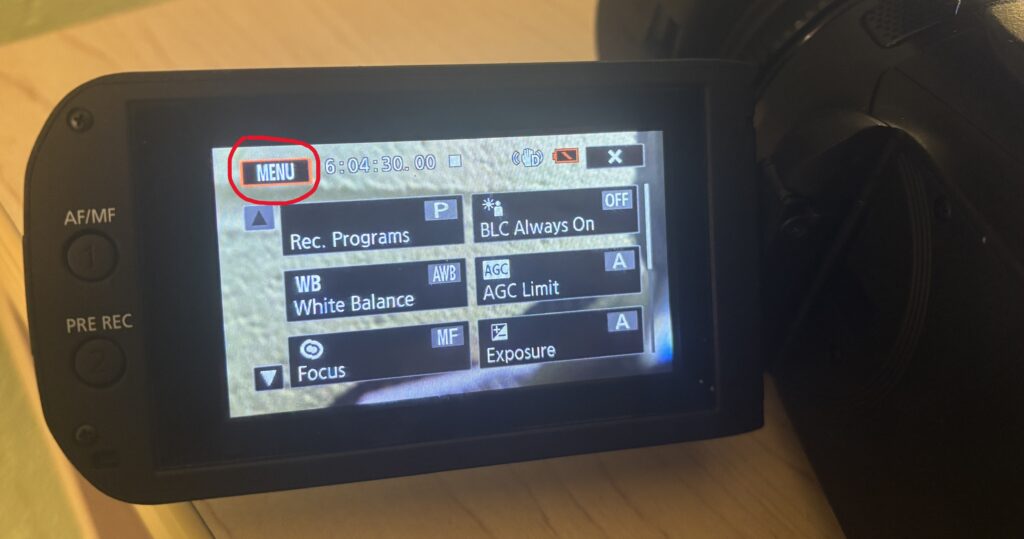
- Press the Home icon on the touchscreen
- Select Recording Setup

- Select Recording Media

- Select the SD card
3. Checking the File Output Type
The camcorder allows you to select your desired recording format before you start recording. By default, the camcorder will record as an mp4 file. This is fine as long as what you’re recording is less than 30 minutes.
Planning to record something longer than 30 minutes? You’ll want to change the format to AVCHD so that your recording isn’t broken up into multiple files. To do so:
- Press the Home icon on the touchscreen
- Navigate to the Recording Setup menu
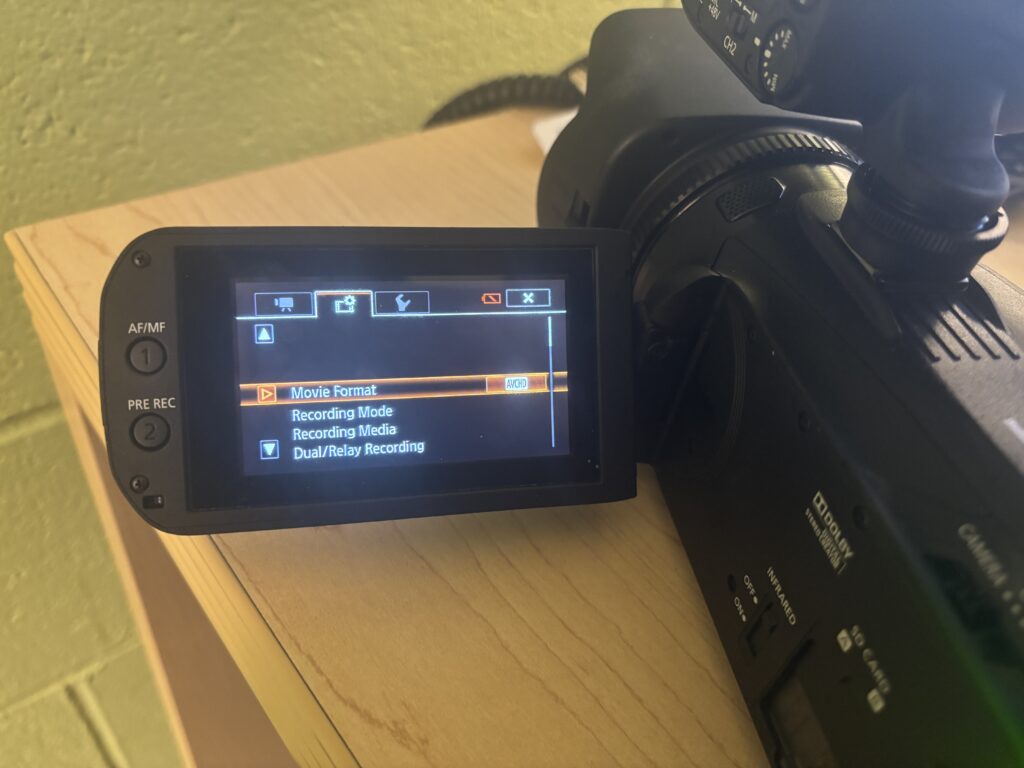
- Select Movie Format
- Select AVCHD and Confirm
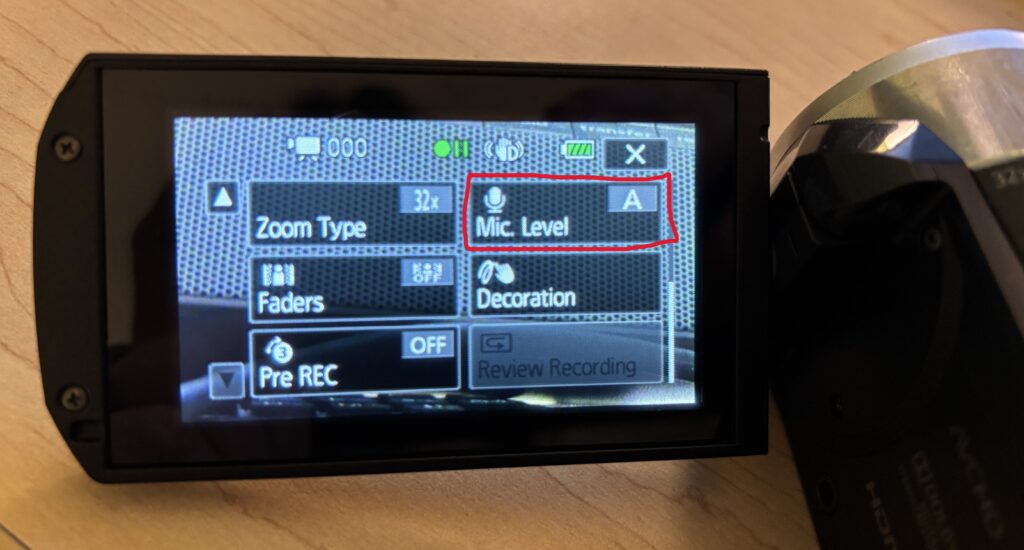
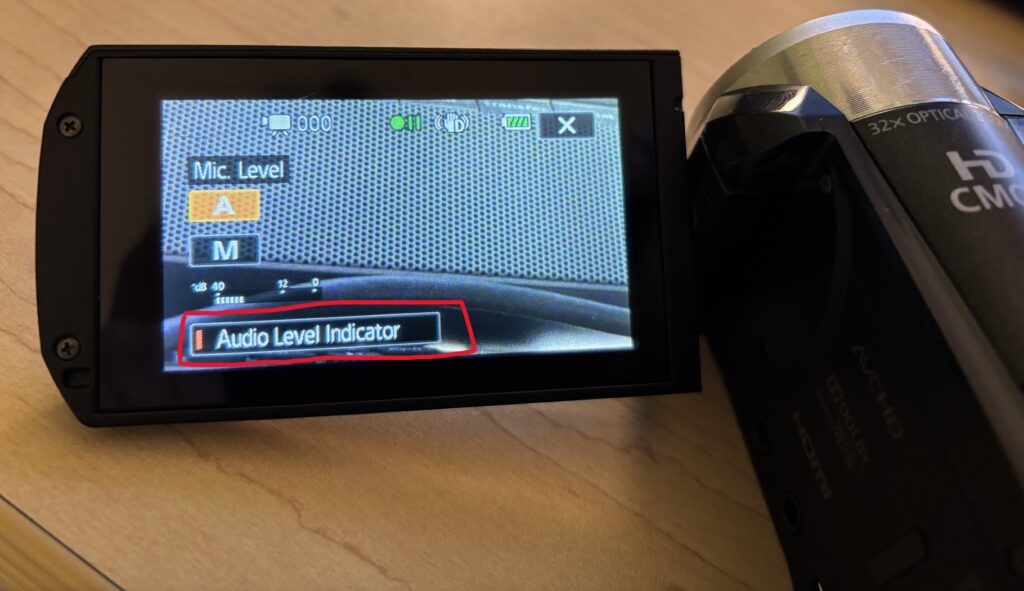
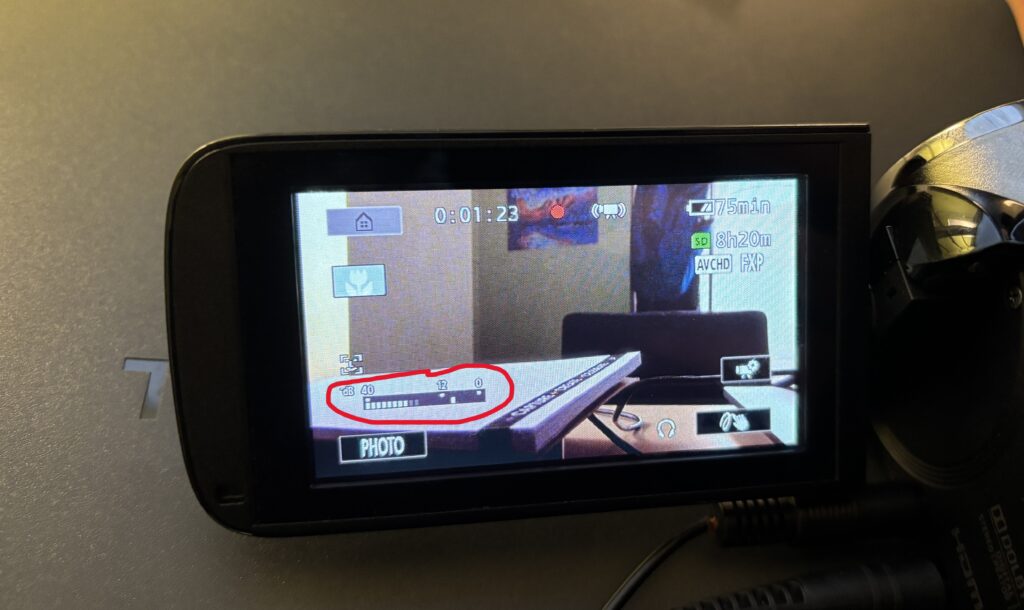
4. Using the Audio Level Indicator
The Audio Level Indicator can help you monitor audio while recording. Once you plug in a microphone, this level will automatically appear on the touchscreen.

5. Recording Video
- Frame your shot using the LCD screen
- Press the Start/Stop button to begin recording
- Press the Start/Stop button again to stop recording
A red recording indicator on the screen confirms when recording is active.
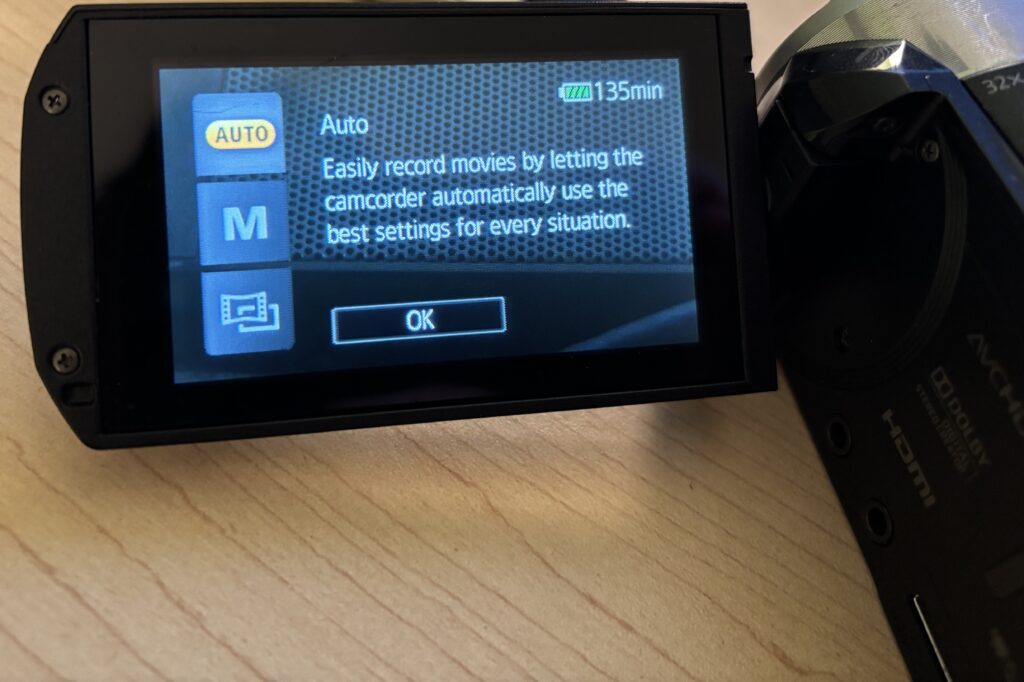
6. Using Auto Mode (Recommended)
For most projects, Auto mode works best.
- Leave the camcorder in Auto mode
- The camera will automatically adjust focus, exposure, and color
- Focus on framing your subject and keeping the camera steady
7. Holding the Camcorder Steady
Stable footage makes a big difference in video quality.
- Use the hand strap for support
- Keep your movements slow and controlled
- Use a tripod for interviews or longer recordings
Avoid fast pans or sudden movements while recording.
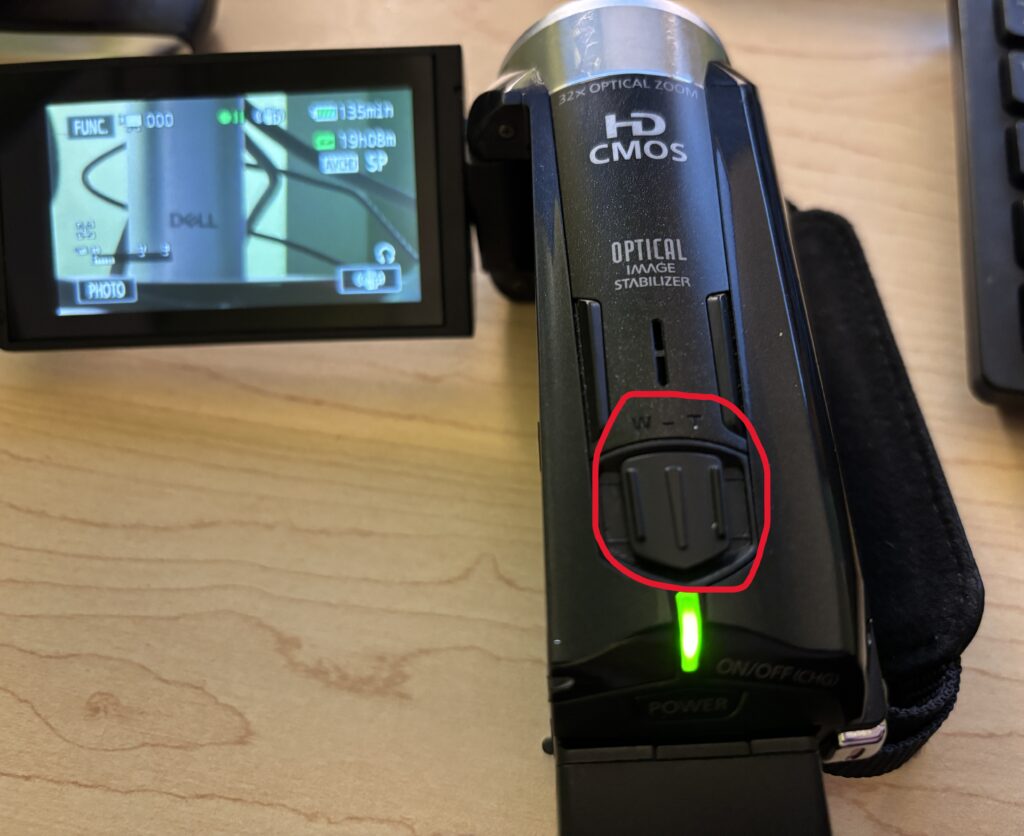
8. Zoom and Focus Tips
- Use the zoom rocker slowly for smooth zooming
- Avoid excessive zooming during recording
- Pause briefly before recording to allow auto-focus to lock
Slow, intentional movement looks more professional on video.
9. Reviewing and Deleting Footage
- Press the Playback button to review recorded clips
- Use the on-screen controls to navigate videos
- Delete unwanted clips to free up storage space
Always review footage before leaving your recording location.
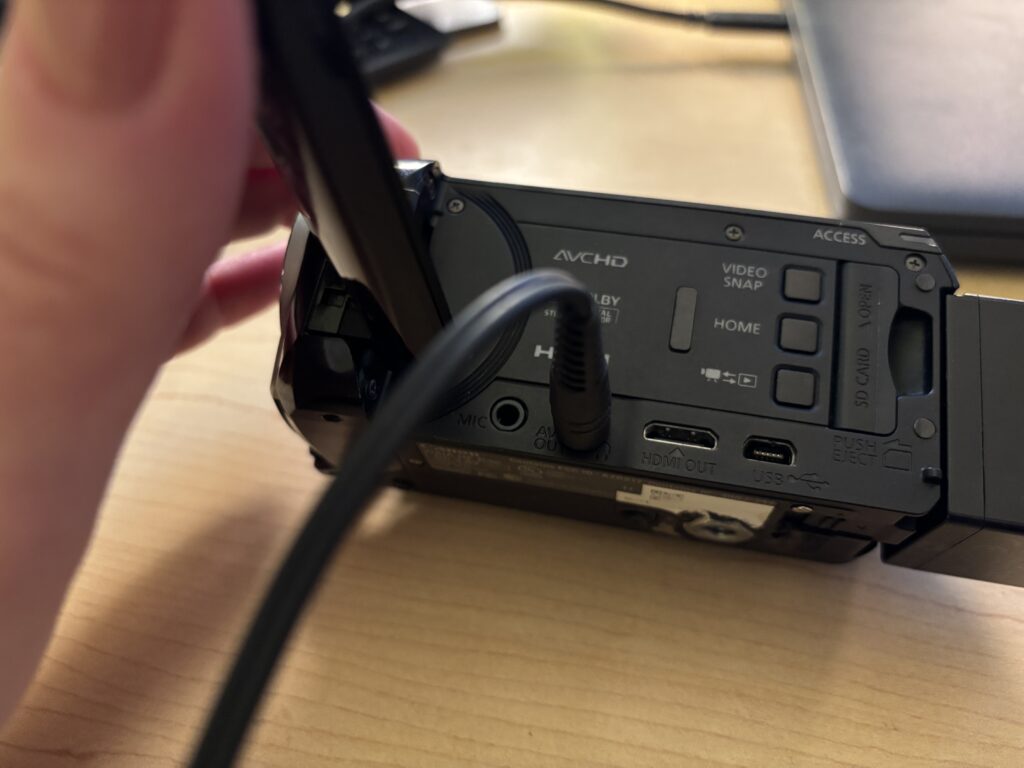
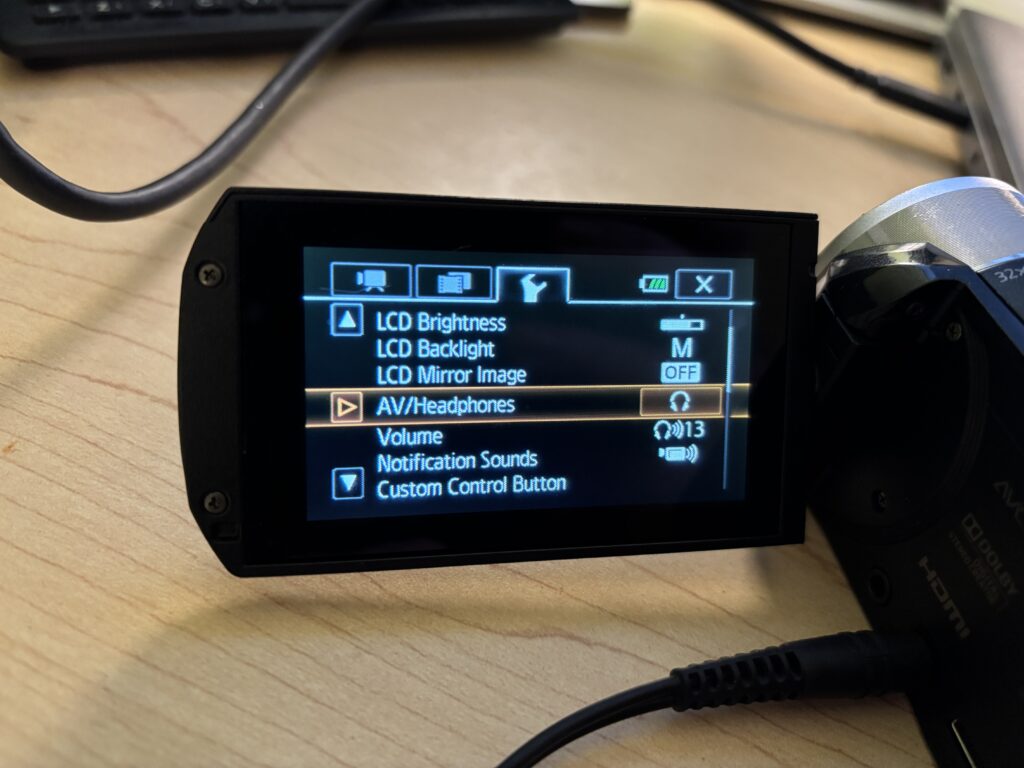
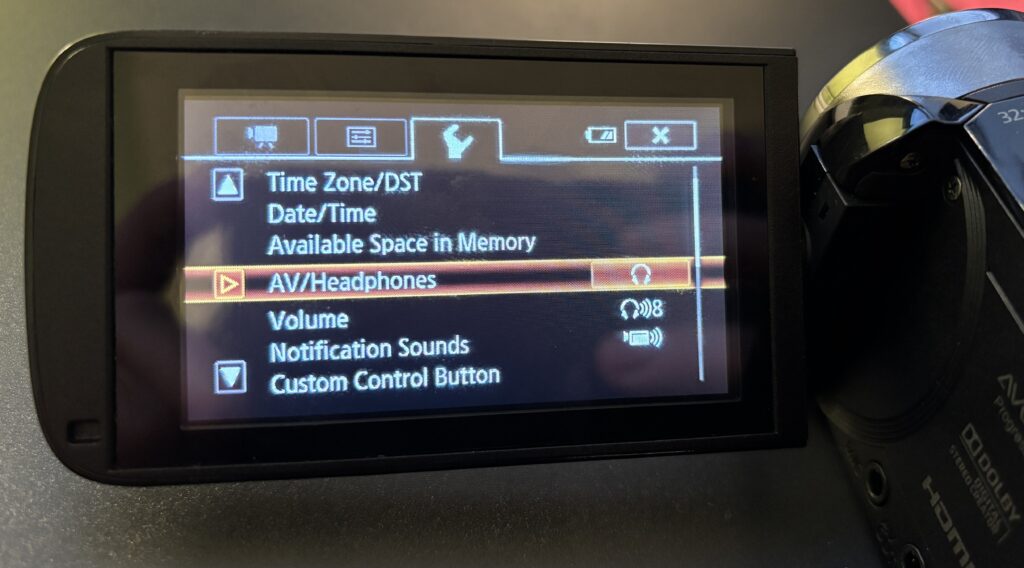
Using Headphones to Monitor Audio
If you’re using headphones to monitor audio during filming and you hear a buzzing noise once the headphones are plugged in, you will need to follow the below steps.
- Click on the Home button in the top left of the touchscreen
- Select Other Settings
- Click the tab at the top with the wrench icon
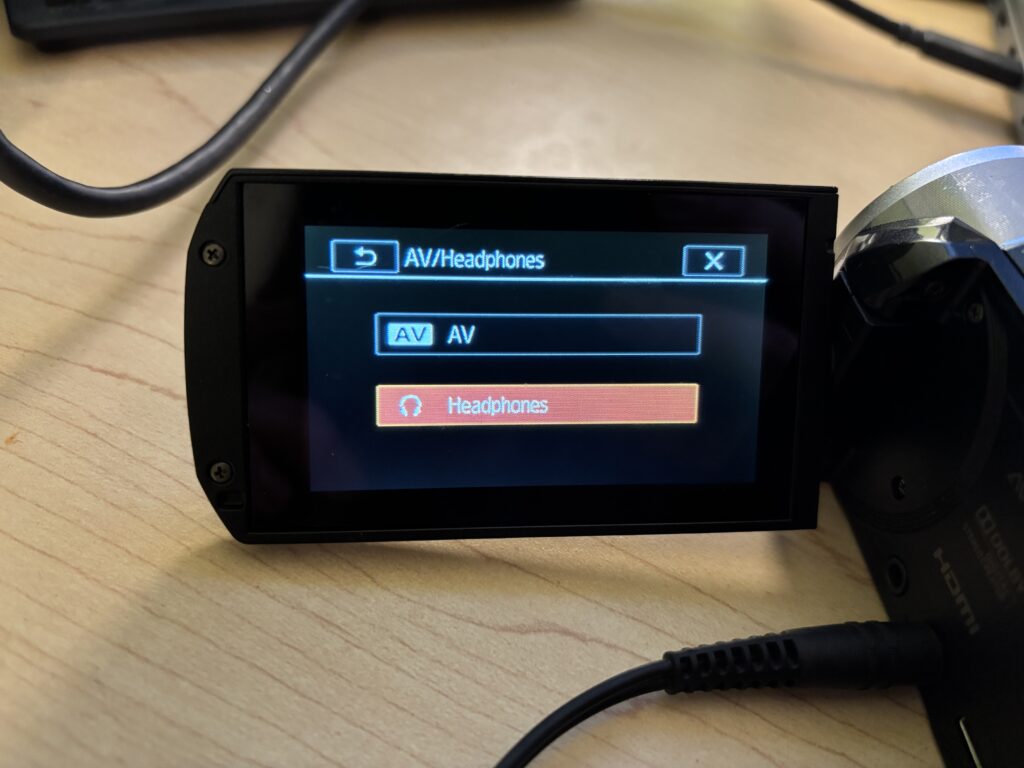
- Select AV/Headphones
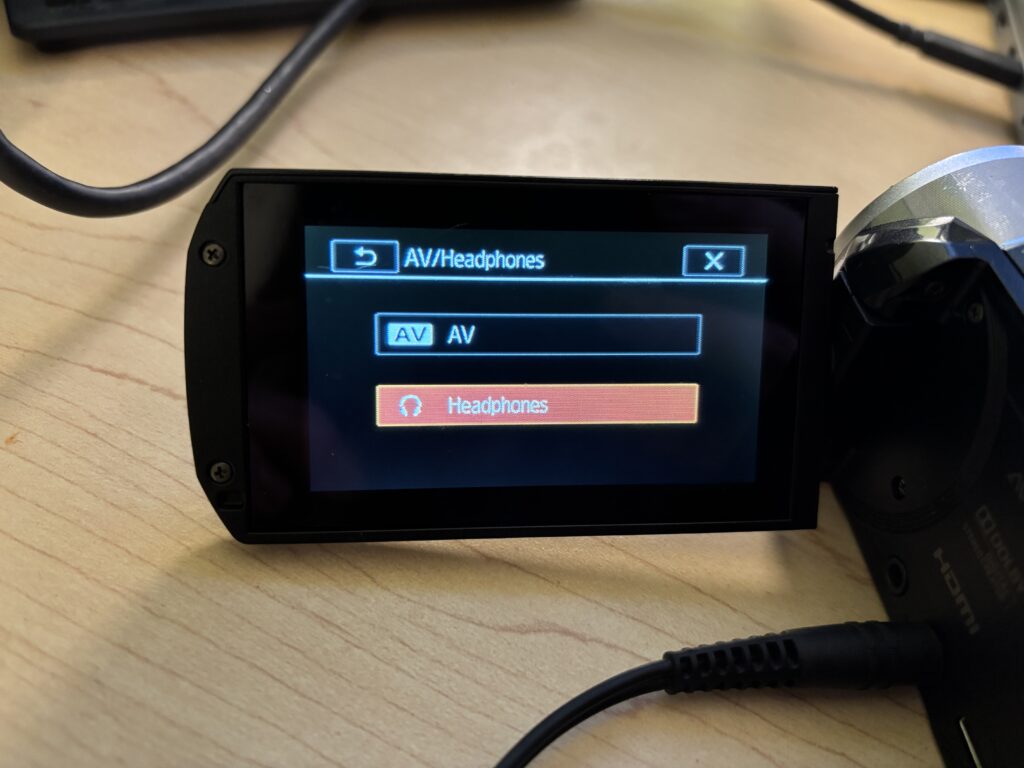
- Select the Headphones option
Helpful Tips
- Record a short test clip before important shoots
- Keep shots simple and steady
- Use a tripod whenever possible
- Check battery life and storage before recording
You’re Ready to Record
The Canon VIXIA HF R50 is designed to make video recording straightforward and reliable. Start in Auto mode, focus on steady shots and clear audio, and you’ll be ready to capture strong video for class projects, interviews, and events.