For Soviet Leadership, the 1957 Moscow World Festival of Youth and Students was a prime opportunity to illustrate the Soviet Union as “an international, active, peace-loving population that was collectively committed to promoting an alternative to American exploitation around the world.” The festival contributors were depended upon to exhibit Soviet Youth as superior, having admirable ethics and awareness. These youth were not only expected to convey these ideals, but also give the impression to the world delegates that they were invigorated by the memorandum in Khrushchev’s 20th Party Congress speech and embody “Soviet openness and international mobilization.” The Youth was supposed to present these sentiments and ideals as “participants who were acting of their own free will” as a means to revise the public assumption of a forcible Soviet government. Margaret Peacock portrays the 1957 festival as endeavoring to “replace older Stalinist visions of grateful, insulated Soviet youngsters with new images of well educated, independent, creative and activist youth” competent of international opposition with capitalism.
Tag Archives: khrushchev
Shrinkage of the Aral Sea: Detrimental Effects
Elizabeth Lowman
When the Bolsheviks came to power in 1917, their rule was marked by the desire to control everything, including nature. What resulted is what demographers Murray Feshbach and Alfred Friendly referred to as “a sixty-year pattern of ecocide by design.”[1] Ecocide is the practice of destroying an environment’s ecosystems. Alternatively, sustainability is the practice of taking no more from the environment than can later be replaced. The Soviet Union abandoned the idea of giving back to the earth by taking as much as they could to make a profit.
Over-irrigation from the Aral Sea was one of the worst instances of Soviet environmental control. During the rule of Nikita Khrushchev, the Soviet Union embarked on the “Virgin Lands Campaign,” which plowed untamed lands to grow food for the Soviet Union. The Soviets realized that the Central Asian nations of Uzbekistan, Turkmenistan, Azerbaijan, and Kazakhstan could be used for growing cotton. Officials called cotton “white gold” and were pleased when the USSR became the second largest cotton producer in the world by the 1980s.[2]
Located between Uzbekistan and Kazakhstan lays the Aral Sea, which was the fourth largest sea in the early 1960s.[3] Two rivers act as tributaries, feeding the sea with water that the Soviet government then used to irrigate cotton. However, since irrigation systems were not designed properly, less and less water began to reach the sea.[4] The result was the Aral Sea shrinking by 44 percent.[5] Fertilizers and pesticides the Soviets fed used on the cotton also contributed to the sea’s shrinkage.
The Soviet Union’s irresponsible cotton growing campaign harmed Central Asia on multiple levels. The shrinkage of the sea destabilized the environment and ecosystem. Public health in Central Asia still is deeply threatened by multiple environmental and social factors introduced by the cotton campaign. Russia’s exploitation of Central Asia caused the Central Asians to believe they were treated as second-class Soviet citizens, leading to political unrest in the region.
The shrinkage of the Aral Sea had devastating consequences for the surrounding environment. These consequences included the destruction of the sea itself, land and water pollution, and increased wind erosion.
Poor Soviet irrigation methods took their toll on the sea, draining it to one third of its former volume. In addition to that, the chemicals, pesticides, and fertilizers fed to the cotton by the Soviets contaminated the remaining water as well as the miles of sand serving as a reminder of the Aral Sea’s former breadth.[6]
The water pollution introduced by these chemicals had a wide range of affects. The salinity of the water is now equivalent to that of an open ocean,[7] six times the limit set forth by the World Health Organization. This affects the quality of drinking water available to those living around the sea. Scientists still are uncertain whether foul tasting water has any detrimental health effects that extremely high salinity can potentially cause,[8] which will be addressed later.
High salinity is not the only problem with the water. Sixty-five percent of the water in Karkalpakstan, a republic in Uzbekistan, does not meet health regulations for pollution.[9] The sea also has high levels of lead and cadmium.[10] While the pollution is most likely harmful to humans, it has definitely proven harmful to fish. All twenty of the important fish species of the Aral Sea have died.[11] Fish kills signify the potential danger of the water but also eliminated a source of food and income to the people inhabiting the area around the sea.
Another environmental problem present in this region, wind erosion, spreads 43 million metric tons of the contaminated sand and silt from around the Aral Sea to the surrounding lands, inhibiting plant growth.[12] The wind erosion has worsened since the 1970s, when the Soviet government forced Central Asian peasants to cut down trees to make room for cotton.[13] With nothing to hold down the soil, wind erosion continues to take its toll on the land.
Intense dust and salt storms are another consequence of wind erosion. In the 1980s, between 90 and 140 million tons of salty sand were carried as far as Belorussia and Afghanistan annually.[14] As will be discussed later, the frequent storms may be causing increasing cases of respiratory problems in the population.[15]
Between poor irrigation, polluting the land and water, and deforestation, the Soviets caused extreme damage to the environment in the pursuit of cotton.
These environmental effects closely tie in with the adverse health affects seen in the population. These health effects include disease outbreaks, contaminated breast milk, and respiratory problems. In the 1980s, many of these problems could be directly attributed to the destruction of Aral Sea, but today, data is inconclusive as to the extent of damage being done to people’s health.
In the past, the drinking water for those that live around the Aral Sea was unfit for human consumption. In the 1980s, “Turkmenistan’s health minister described the Turkmen canal, a major source of drinking water, as an open sewer after finding impermissibly high bacteria counts in 60 to 98 percent of all water samples taken from it.”[16] In addition to pesticides, fertilizer runoff introduced bacteria into the water. Diseases such as hepatitis, typhoid, dysentery, and cancer plagued the population. According to some counts, “hepatitis…afflicted seven out of every ten inhabitants.”[17] These diseases were either caused by waterborne bacteria and viruses, or by heavy metal deposits found in the water.
As discussed earlier, scientists today are unsure if the drinking water is still dangerous to humans, although they find it quite possible. However, scientists do know that Central Asia has an extremely high infant mortality rate, with infants dying of upper respiratory infections, diarrhea, tuberculosis, and malnutrition. Contaminated water is a likely suspect for outbreaks of diarrhea. The World Health Organization also expressed concern that the Aral Sea region lacks a steady and safe water supply, which is unsafe for children.[18]
High infant mortality could also be a result of contaminated breast milk in mothers. Scientists found the milk to be contaminated with PCBs and other pesticides the Soviets used on the land after a study they performed in Kazakhstan. Scientists hypothesize women come into contact with these chemicals by eating fish from areas of high water pollution, as well as through agricultural products that are grown with pesticides.[19] However, the amount of PCBs and other pesticides detected were still less than amounts found in industrialized nations, with the exception of in Atyrau, a city in Kazakhstan, where the amount of pesticides were found to be the same as in industrialized nations.[20] Currently, the toxicity of the breast milk is inconclusive, but in the late 1980s, doctors warned Turkmen mothers against breast-feeding because of toxic milk.[21] Today, many Central Asian women are reluctant to breast-feed their infants.
As previously mentioned, the frequent dust storms seen in Central Asia can have ill effects on people’s health. The Aral Sea Dust and Respiratory Disease Project sought to find a correlation between the environment and public health. Respiratory diseases are responsible for many illnesses and deaths in Central Asia. In fact “fifty percent of all illnesses in children are respiratory.”[22] From 2000-2001, researchers discovered that dust inhalation in Central Asia was dramatically beyond the guidelines of the Environmental Protection Agency in the United States. Overall, the results were inconclusive, as more respiratory infections occurred farther from the Aral Sea, possibly caused by other sources or by the ability of dust to travel. Researchers hypothesized that not all dust was from the Aral Sea, but most of the dust in the late summer dust storms was likely from this region.[23]
The link between environmental damage and public health disasters was strongly established in the 1980s as chemicals, pesticides, and bacteria poisoned many Central Asians. While this link is not as clear today, many researchers believe Central Asians are still suffering because of the environment.
Because of the damage being done to their land and their health, Central Asians began to resent Russia, causing political issues. Moscow’s complete disregard for the region’s plight was “a measure of the second class status” of the predominately Muslim Central Asian states.[24] Because Central Asia is religiously and ethnically different from Eastern Europe, the Soviet government cared little about the issues Central Asia faced. As well as destroying the land for profit, the Soviet government refused to give Central Asians adequate medical care. “In the four [Central Asian] republics together in 1987 there were, on average, fewer than 14 pediatricians for every 10,000 children,” a fraction of what was seen in the rest of the Soviet Union.[25]
At first, Central Asians cooperated, but they soon began to defend their rights as Soviets. Spokespeople accused Moscow of genocide. Nationalists demanded Moscow redirect Siberian rivers to Central Asia to provide clean drinking water. Uzbek nationalist groups, originally concerned with promoting the Uzbek language, expanded their campaigns to include environmental reforms. Journalists wrote of malnourished children. In an attempt to pacify what they perceived as a potential revolt, the government would make promises and send aid. However, the promises were not kept and the aid was unsubstantial. Although the republics of Central Asia declared their independence in 1991, relations with Russia still remain icy, in part due to the Virgin Lands Campaign.[26]
Some progress has been made in recent years to rehabilitate the Aral Sea. In 1999, the World Bank launched a project in which it built a 13-kilometer dike in one of the Aral Sea’s tributaries to raise sea level and decrease salinity. The project went even better than expected, with the tributary reaching the intended level within only seven months, as well as the its capacity doubling to 700 cubic meters per second. The next goal, set forth by Kazakh president Nursultan Nazarbayev, is to raise the sea level of the northern sea four to six more meters.[27] For the first time in decades, the world is feeling more optimistic about the plight of the Aral Sea.
The Soviet Union’s fierce desire to control nature with no regard to sustainability destroyed the environment, the health of Soviet citizens, and Russian-Central Asian relations. Though optimism about the region is growing, it is unlikely the Aral Sea will ever return to its former glory. The Soviet Union ruthlessly exploited the land for profit, and decades later; Central Asians are still paying the price.
Notes
1.Murray Feshbach and Alfred Friendly, Jr. Ecocide in the USSR: Health and Nature under Siege (New York: Basic Books, 1992), 75.
2. Feshbach and Friendly, Ecocide in the USSR, 74.
3. Kerstin Lindahl Kiessling. “Conference on the Aral Sea: Women, Children, Health and Environment,” Ambio 27, no. 7 (1998): 560.
4. Ian Small, J. van der Meer and R.E.G. Upshur. “Acting on Environmental Health Disaster: The Case of the Aral Sea,” Environmental Health Perspectives 109, no. 6 (2001): 547.
5. Feshbach and Friendly, Ecocide in the USSR, 74.
6. Kiessling “Conference on the Aral Sea, “ 560.
7. Kiessling “Conference on the Aral Sea,” 560.
8. Small, et al., “Acting on Environmental Health Disaster,” 548.
9. Small, et al., “Acting on Environmental Health Disaster,” 548.
10. Giles F.S. Wiggs, Sarah L. O’hara, Johannah Wegerdt, Joost Van Der Meer, Ian Small and Richard Hubbard. “The Dynamics and Characteristics of Aeolian Dust in Dryland Central Asia: Possible Impacts on Human Exposure and Respiratory Health in the Aral Sea Basin,” The Geographical Journal 169, no. 2 (2003): 143.
11. Small, et al., “Acting on Environmental Health Disaster,” 548.
12. Kiessling, “Conference on the Aral Sea,” 560.
13. Feshbach and Friendly, Ecocide in the USSR, 77.
14. Feshbach and Friendly, Ecocide in the USSR, 75.
15. Wiggs, et al., “The Dynamics and Characteristics of Aeolian Dust,” 143.
16. Feshbach and Friendly, Ecocide in the USSR, 76-77.
17. Feshbach and Friendly, Ecocide in the USSR, 77.
18. Kiessling, “Conference on the Aral Sea,” 563.
19. Kim Hooper, Myrto X. Petreas, Jianwen She, Pat Visita, Jennifer Winkler, Michael McKinney, Mandy Mok, Fred Sy, Jarnail Garcha, Modan Gill, Robert D. Stephens, Gulnara Semenova, Turgeledy Sharmanov and Tamara Chuvakova. “Analysis of Breast Milk to Assess Exposure to Chlorinated Contaminants in Kazakhstan: PCBs and Organochlorine Pesticides in Southern Kazakhstan,” Environmental Health Perspectives 105, no. 11 (1997): 1250.
20. Hooper, et al., “Analysis of Breast Milk,” 1254.
21. Feshbach and Friendly, Ecocide in the USSR, 73.
22. Wiggs, et al., “The Dynamics and Characteristics of Aeolian Dust,” 143.
23. Wiggs, et al., “The Dynamics and Characteristics of Aeolian Dust,” 152-155.
24. Feshbach and Friendly, Ecocide in the USSR, 75.
25. Feshbach and Friendly, Ecocide in the USSR, 81.
26. Feshbach and Friendly, Ecocide in the USSR, 83-88.
27. Christopher Pala, “Once a Terminal Case, the North Aral Sea Shows New Signs of Life,” Science 312, no. 6 (2001): 183.
Works Cited:
 Aral Sea dust storm from space (NASA)
Aral Sea dust storm from space (NASA)
 Ship on the remains of the Aral Sea in Kazakhstan (Wikipedia Commons)
Ship on the remains of the Aral Sea in Kazakhstan (Wikipedia Commons)
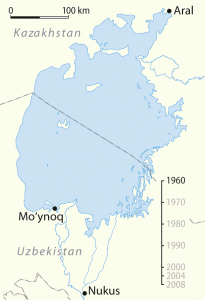 Moving map showing the shrinkage of the Aral Sea (Wikipedia Commons)
Moving map showing the shrinkage of the Aral Sea (Wikipedia Commons)
Video:
The Dissident Movement in the Soviet Union
Soviet intellectuals in the late 1960s and early ’70s decided it was high time to voice their opposition to the current political situation in the Union. The movement had roots in the Khrushchev era when the state loosened controls ever so slightly, but by the time Brezhnev came to power and tried to restrict expression yet again, the movement was already taking off.
It was a period of both hope and desperation. For the dissidents, there was hope. Their public protests and demonstrations against the Soviet state system only further emboldened their radical thinking; they believed they were the “conscience of society” and had a duty to stand up and demand freedoms for the people of Russia. The dissidents sought democratic socialism and political liberalism, while condemning western ideologies that overshadowed Russian Orthodox values.
Roy Medvedev, a dissident movement leader.
Credit: www.soviethistory.org
For the Soviet authorities, desperation was in the air. Their legitimacy was being called into question and they could not afford that. Their attempts at controlling the dissidents were tried and true Soviet tactics: confiscating literature, exiling leaders, condemning offenders to prison or mental institutions, removing dissidents from their occupations, and launching propaganda campaigns to counter and delegitimize dissident ideology.
The actual number of dissidents may have been small, but their impact was disproportionately large. The Soviet’s attempts to regain control of public thought were desperate and futile, and if there is one thing I have learned from studying history, it is that desperate actions of a government mark the beginning of the end. I would not go so far as to credit the dissident movement with being the final nail in the coffin of the Soviet Union. However, it was another blow to their ideology and power, and it is a movement that ought not to be overlooked.
Khrushchev’s Unintended Consequences
In response to Khrushchev’s denunciation of Stalin in Moscow, as well as to the growing discontent at home, citizens of Poland, Hungary and eventually Czechoslovakia.
Poland: June 1956
Workers broke out in protest against the unpopular Communist regime and demanded better pay and treatment at the hands of the government. The demonstrations eventually fizzled out thanks to the reformist Wladyslaw Gomulka, who worked with Soviet leaders and the Polish Communist Party to appease the workers and avoid a revolution.
Hungary: October 1956
A year prior, Hungarian’s liberal leader Imre Nagy was removed from power by supporters of his previous opponent Matyas Rakosi (who had run Hungary up until 1953, when Nagy took power). Discontent continued to grow until October of 1956 when students who had followed the protests in Hungary staged a demonstration that turned violent. The violence soon grew out of hand with rebels arming themselves and forming councils to take over factories. Soviet forces were a part of the initial struggle but it wasn’t until October 31st that Khrushchev decided that a full invasion was necessary to control the situation. Nagy, who had been restored as Prime Minister on the 24th, frantically declared Hungary’s withdrawal from the Warsaw Pact in an attempt to place himself at the center of the revolutionaries resistance. Nagy was eventually captured, tried and executed by the Soviets, along with other insurgent leaders.
Czechoslovakia: 1968
Alexander Dubcek became First Secretary of Czechoslovakia in January 1968 and brought with him the promise of “socialism with a human face.” His grand vision of reform was most unwelcome to the Soviets, who not only feared what could happen in Czechoslovakia, but also what would happen if the wave of reform spread to the Union itself. Soviet officials tried to force Dubcek to abandon his reform plans but he argued that it was too late–the people had too much momentum to accept a return to old ways. In late August the Politburo launched a joint-Warsaw Pact invasion of Czechoslovakia to contain the situation.
This invasion translated into the new Brezhnev Doctrine, which asserted the rights of “the right and responsibility of Communist parties of fraternal socialist countries to intervene against anti-socialist degeneration.” (www.soviethistory.org) Although the invasion was relatively violent-free, the reform movement was squashed and would not regain momentum for quite a while.
Shhhh…It’s a Secret Speech
Khrushchev’s secret speech, given to party officials but not published for the general public, showed his desire for de-Stalinization. Basically, Khrushchev has the same criticisms about Stalin that the rest of the world had: he was paranoid, rude, and killed too many people. Khrushchev believed that Stalin had given the world a bad example of socialism. He also stated that many innocent lives had been lost.
When Khrushchev is speaking, he is careful to maintain the language of the party. He emphasizes the point that Lenin didn’t like Stalin. If Lenin, who cannot be wrong, disliked Stalin, than logically this must mean that Stalin was a bad person. Since Lenin expressly stated he did not want Stalin to be the next leader of the USSR, then Stalin’s reign could be viewed as a mistake and a break away from communism. Khrushchev makes it seem as though a communist must choose between Lenin and Stalin. And a good communist will always choose Lenin.
My questions after reading the speech were these: Did Khrushchev dislike Stalin because Lenin disliked him? Or was this speech, as I suspect, a cleverly designed mask for deeper feelings? Did Khrushchev dislike Stalin for the obvious, ethical reasons? Or personal reasons? Whatever the reason, conditions in the Soviet Union began to improve under de-Stalinization.
Secret Speech
We’ve talked about Khrushchev’s contradicting opinions of Stalin while he was the Party First Secretary and later Chairmen of the USSR, but his “Secret Speech” seems to finally put to rest his true opinion on Stalin’s dictatorship. The speech was known as such because it was read in a session without discussion and was not reported in the Soviet press. However, the Communist world knew of its existence and the claims within- that Stalin’s “Cult of Personality” was responsible of crimes such as the Terror of the later 1930s to the deportation of nationalities in the early 1940s- shocked and led many Western Communists to abandon Communism altogether. Not only did this speech reveal how Khrushchev truly felt about Stalin’s dictatorship and his desire to create a more Leninist society but also consolidated his authority over other Stalinist Party members.
Khrushchev’s speech argued that Stalin’s role in the Party was completely the opposite of the spirit of Marxism-Leninism, thus blaming for the various crimes in the past three decades. He also claimed Lenin recognized Stalin’s negative qualities which made him a poor leader as early as 1922. He spoke of Stalin’s continuous violence and suspicious nature as leading reasons why the Soviet Union suffered such great losses during the war without necessary preparation. His final message is of the abolishment of the “cult of the individual” in favor of the unity of the Party. Ultimately, he is condemning the small role Leninism has played within the government and the atrocities committed under the name of Marxism-Leninism and Stalin.

