Tag Archives: environment
Final Podcast
Disappearing Culture: Indigenous Tribes in the Noril’sk Region of Siberia
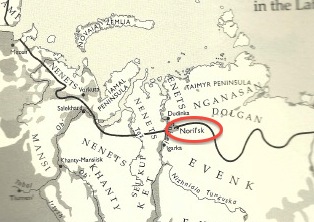
Early in the Soviet era, the government paid little attention to the indigenous tribes of Siberia and did not take into account whether their policies for modernization would have a negative effect on the native peoples. Collectivization and the push for industrialization directly affected the tribes’ economic activity, traditional lifestyle, and the environment in which they lived. Industrialization took place across the Soviet Union, however I have chosen to focus on the city of Noril’sk, located in Krasnoyarsk Krai in northern Siberia, between the Yenisei River and the Taimyr Peninsula. Four main indigenous groups converge in the area of Noril’sk; these groups are the Dolgan, the Nenets, the Nganasan, and the Evenk people. As a result of Soviet collectivization and industrialization policies of the mid-twentieth century, the traditional culture of these indigenous groups altered or faded considerably.
Here is a map showing the geographical location of Noril’sk:
Source: www.thenytimes.com
A key component of analyzing these policies and their effects on these four tribes is to consider the sustainability of these policies with regards to both the environment and the tribes’ traditional ways of life. I would like to clarify that I am defining sustainability as “long-term cultural, economic and environmental health and vitality….together with the importance of linking our social, financial and environmental well-being.” This definition comes from the organization Sustainable Seattle.[1] I argue that Soviet policy towards the indigenous tribes of Siberia in the twentieth century did not promote long-term cultural, economic or environmental vitality, and were therefore unsustainable and unsupportive for the indigenous clans of the region.
Below is a map showing the location of Evenk, Dolgan, Nenet and Nganasan territory relative to Noril’sk and to each other:
The map above shows that Noril’sk serves as a sort of epicenter for these four groups: the Dolgans, Nenets, Nganasans, and Evenks. To learn more about a specific group please click the hyperlinks for further reading. Not only are these four clans close in proximity, but also—like many Siberian tribes—each clan has historically depended on reindeer hunting or herding for their economic livelihood. This does not mean these groups are all the same; they descend from different Eurasian or East Asian ethnic groups and each speak their own native language, among other differences. That being said, each clan experienced similar difficulties adjusting their traditional lifestyles during collectivization and industrialization. There are many ways in which the Soviet Union altered the lives of tribal people in Siberia; collectivization and industrialization are simply the two policies I have chosen to analyze.
Shrinkage of the Aral Sea: Detrimental Effects
Elizabeth Lowman
When the Bolsheviks came to power in 1917, their rule was marked by the desire to control everything, including nature. What resulted is what demographers Murray Feshbach and Alfred Friendly referred to as “a sixty-year pattern of ecocide by design.”[1] Ecocide is the practice of destroying an environment’s ecosystems. Alternatively, sustainability is the practice of taking no more from the environment than can later be replaced. The Soviet Union abandoned the idea of giving back to the earth by taking as much as they could to make a profit.
Over-irrigation from the Aral Sea was one of the worst instances of Soviet environmental control. During the rule of Nikita Khrushchev, the Soviet Union embarked on the “Virgin Lands Campaign,” which plowed untamed lands to grow food for the Soviet Union. The Soviets realized that the Central Asian nations of Uzbekistan, Turkmenistan, Azerbaijan, and Kazakhstan could be used for growing cotton. Officials called cotton “white gold” and were pleased when the USSR became the second largest cotton producer in the world by the 1980s.[2]
Located between Uzbekistan and Kazakhstan lays the Aral Sea, which was the fourth largest sea in the early 1960s.[3] Two rivers act as tributaries, feeding the sea with water that the Soviet government then used to irrigate cotton. However, since irrigation systems were not designed properly, less and less water began to reach the sea.[4] The result was the Aral Sea shrinking by 44 percent.[5] Fertilizers and pesticides the Soviets fed used on the cotton also contributed to the sea’s shrinkage.
The Soviet Union’s irresponsible cotton growing campaign harmed Central Asia on multiple levels. The shrinkage of the sea destabilized the environment and ecosystem. Public health in Central Asia still is deeply threatened by multiple environmental and social factors introduced by the cotton campaign. Russia’s exploitation of Central Asia caused the Central Asians to believe they were treated as second-class Soviet citizens, leading to political unrest in the region.
The shrinkage of the Aral Sea had devastating consequences for the surrounding environment. These consequences included the destruction of the sea itself, land and water pollution, and increased wind erosion.
Poor Soviet irrigation methods took their toll on the sea, draining it to one third of its former volume. In addition to that, the chemicals, pesticides, and fertilizers fed to the cotton by the Soviets contaminated the remaining water as well as the miles of sand serving as a reminder of the Aral Sea’s former breadth.[6]
The water pollution introduced by these chemicals had a wide range of affects. The salinity of the water is now equivalent to that of an open ocean,[7] six times the limit set forth by the World Health Organization. This affects the quality of drinking water available to those living around the sea. Scientists still are uncertain whether foul tasting water has any detrimental health effects that extremely high salinity can potentially cause,[8] which will be addressed later.
High salinity is not the only problem with the water. Sixty-five percent of the water in Karkalpakstan, a republic in Uzbekistan, does not meet health regulations for pollution.[9] The sea also has high levels of lead and cadmium.[10] While the pollution is most likely harmful to humans, it has definitely proven harmful to fish. All twenty of the important fish species of the Aral Sea have died.[11] Fish kills signify the potential danger of the water but also eliminated a source of food and income to the people inhabiting the area around the sea.
Another environmental problem present in this region, wind erosion, spreads 43 million metric tons of the contaminated sand and silt from around the Aral Sea to the surrounding lands, inhibiting plant growth.[12] The wind erosion has worsened since the 1970s, when the Soviet government forced Central Asian peasants to cut down trees to make room for cotton.[13] With nothing to hold down the soil, wind erosion continues to take its toll on the land.
Intense dust and salt storms are another consequence of wind erosion. In the 1980s, between 90 and 140 million tons of salty sand were carried as far as Belorussia and Afghanistan annually.[14] As will be discussed later, the frequent storms may be causing increasing cases of respiratory problems in the population.[15]
Between poor irrigation, polluting the land and water, and deforestation, the Soviets caused extreme damage to the environment in the pursuit of cotton.
These environmental effects closely tie in with the adverse health affects seen in the population. These health effects include disease outbreaks, contaminated breast milk, and respiratory problems. In the 1980s, many of these problems could be directly attributed to the destruction of Aral Sea, but today, data is inconclusive as to the extent of damage being done to people’s health.
In the past, the drinking water for those that live around the Aral Sea was unfit for human consumption. In the 1980s, “Turkmenistan’s health minister described the Turkmen canal, a major source of drinking water, as an open sewer after finding impermissibly high bacteria counts in 60 to 98 percent of all water samples taken from it.”[16] In addition to pesticides, fertilizer runoff introduced bacteria into the water. Diseases such as hepatitis, typhoid, dysentery, and cancer plagued the population. According to some counts, “hepatitis…afflicted seven out of every ten inhabitants.”[17] These diseases were either caused by waterborne bacteria and viruses, or by heavy metal deposits found in the water.
As discussed earlier, scientists today are unsure if the drinking water is still dangerous to humans, although they find it quite possible. However, scientists do know that Central Asia has an extremely high infant mortality rate, with infants dying of upper respiratory infections, diarrhea, tuberculosis, and malnutrition. Contaminated water is a likely suspect for outbreaks of diarrhea. The World Health Organization also expressed concern that the Aral Sea region lacks a steady and safe water supply, which is unsafe for children.[18]
High infant mortality could also be a result of contaminated breast milk in mothers. Scientists found the milk to be contaminated with PCBs and other pesticides the Soviets used on the land after a study they performed in Kazakhstan. Scientists hypothesize women come into contact with these chemicals by eating fish from areas of high water pollution, as well as through agricultural products that are grown with pesticides.[19] However, the amount of PCBs and other pesticides detected were still less than amounts found in industrialized nations, with the exception of in Atyrau, a city in Kazakhstan, where the amount of pesticides were found to be the same as in industrialized nations.[20] Currently, the toxicity of the breast milk is inconclusive, but in the late 1980s, doctors warned Turkmen mothers against breast-feeding because of toxic milk.[21] Today, many Central Asian women are reluctant to breast-feed their infants.
As previously mentioned, the frequent dust storms seen in Central Asia can have ill effects on people’s health. The Aral Sea Dust and Respiratory Disease Project sought to find a correlation between the environment and public health. Respiratory diseases are responsible for many illnesses and deaths in Central Asia. In fact “fifty percent of all illnesses in children are respiratory.”[22] From 2000-2001, researchers discovered that dust inhalation in Central Asia was dramatically beyond the guidelines of the Environmental Protection Agency in the United States. Overall, the results were inconclusive, as more respiratory infections occurred farther from the Aral Sea, possibly caused by other sources or by the ability of dust to travel. Researchers hypothesized that not all dust was from the Aral Sea, but most of the dust in the late summer dust storms was likely from this region.[23]
The link between environmental damage and public health disasters was strongly established in the 1980s as chemicals, pesticides, and bacteria poisoned many Central Asians. While this link is not as clear today, many researchers believe Central Asians are still suffering because of the environment.
Because of the damage being done to their land and their health, Central Asians began to resent Russia, causing political issues. Moscow’s complete disregard for the region’s plight was “a measure of the second class status” of the predominately Muslim Central Asian states.[24] Because Central Asia is religiously and ethnically different from Eastern Europe, the Soviet government cared little about the issues Central Asia faced. As well as destroying the land for profit, the Soviet government refused to give Central Asians adequate medical care. “In the four [Central Asian] republics together in 1987 there were, on average, fewer than 14 pediatricians for every 10,000 children,” a fraction of what was seen in the rest of the Soviet Union.[25]
At first, Central Asians cooperated, but they soon began to defend their rights as Soviets. Spokespeople accused Moscow of genocide. Nationalists demanded Moscow redirect Siberian rivers to Central Asia to provide clean drinking water. Uzbek nationalist groups, originally concerned with promoting the Uzbek language, expanded their campaigns to include environmental reforms. Journalists wrote of malnourished children. In an attempt to pacify what they perceived as a potential revolt, the government would make promises and send aid. However, the promises were not kept and the aid was unsubstantial. Although the republics of Central Asia declared their independence in 1991, relations with Russia still remain icy, in part due to the Virgin Lands Campaign.[26]
Some progress has been made in recent years to rehabilitate the Aral Sea. In 1999, the World Bank launched a project in which it built a 13-kilometer dike in one of the Aral Sea’s tributaries to raise sea level and decrease salinity. The project went even better than expected, with the tributary reaching the intended level within only seven months, as well as the its capacity doubling to 700 cubic meters per second. The next goal, set forth by Kazakh president Nursultan Nazarbayev, is to raise the sea level of the northern sea four to six more meters.[27] For the first time in decades, the world is feeling more optimistic about the plight of the Aral Sea.
The Soviet Union’s fierce desire to control nature with no regard to sustainability destroyed the environment, the health of Soviet citizens, and Russian-Central Asian relations. Though optimism about the region is growing, it is unlikely the Aral Sea will ever return to its former glory. The Soviet Union ruthlessly exploited the land for profit, and decades later; Central Asians are still paying the price.
Notes
1.Murray Feshbach and Alfred Friendly, Jr. Ecocide in the USSR: Health and Nature under Siege (New York: Basic Books, 1992), 75.
2. Feshbach and Friendly, Ecocide in the USSR, 74.
3. Kerstin Lindahl Kiessling. “Conference on the Aral Sea: Women, Children, Health and Environment,” Ambio 27, no. 7 (1998): 560.
4. Ian Small, J. van der Meer and R.E.G. Upshur. “Acting on Environmental Health Disaster: The Case of the Aral Sea,” Environmental Health Perspectives 109, no. 6 (2001): 547.
5. Feshbach and Friendly, Ecocide in the USSR, 74.
6. Kiessling “Conference on the Aral Sea, “ 560.
7. Kiessling “Conference on the Aral Sea,” 560.
8. Small, et al., “Acting on Environmental Health Disaster,” 548.
9. Small, et al., “Acting on Environmental Health Disaster,” 548.
10. Giles F.S. Wiggs, Sarah L. O’hara, Johannah Wegerdt, Joost Van Der Meer, Ian Small and Richard Hubbard. “The Dynamics and Characteristics of Aeolian Dust in Dryland Central Asia: Possible Impacts on Human Exposure and Respiratory Health in the Aral Sea Basin,” The Geographical Journal 169, no. 2 (2003): 143.
11. Small, et al., “Acting on Environmental Health Disaster,” 548.
12. Kiessling, “Conference on the Aral Sea,” 560.
13. Feshbach and Friendly, Ecocide in the USSR, 77.
14. Feshbach and Friendly, Ecocide in the USSR, 75.
15. Wiggs, et al., “The Dynamics and Characteristics of Aeolian Dust,” 143.
16. Feshbach and Friendly, Ecocide in the USSR, 76-77.
17. Feshbach and Friendly, Ecocide in the USSR, 77.
18. Kiessling, “Conference on the Aral Sea,” 563.
19. Kim Hooper, Myrto X. Petreas, Jianwen She, Pat Visita, Jennifer Winkler, Michael McKinney, Mandy Mok, Fred Sy, Jarnail Garcha, Modan Gill, Robert D. Stephens, Gulnara Semenova, Turgeledy Sharmanov and Tamara Chuvakova. “Analysis of Breast Milk to Assess Exposure to Chlorinated Contaminants in Kazakhstan: PCBs and Organochlorine Pesticides in Southern Kazakhstan,” Environmental Health Perspectives 105, no. 11 (1997): 1250.
20. Hooper, et al., “Analysis of Breast Milk,” 1254.
21. Feshbach and Friendly, Ecocide in the USSR, 73.
22. Wiggs, et al., “The Dynamics and Characteristics of Aeolian Dust,” 143.
23. Wiggs, et al., “The Dynamics and Characteristics of Aeolian Dust,” 152-155.
24. Feshbach and Friendly, Ecocide in the USSR, 75.
25. Feshbach and Friendly, Ecocide in the USSR, 81.
26. Feshbach and Friendly, Ecocide in the USSR, 83-88.
27. Christopher Pala, “Once a Terminal Case, the North Aral Sea Shows New Signs of Life,” Science 312, no. 6 (2001): 183.
Works Cited:
 Aral Sea dust storm from space (NASA)
Aral Sea dust storm from space (NASA)
 Ship on the remains of the Aral Sea in Kazakhstan (Wikipedia Commons)
Ship on the remains of the Aral Sea in Kazakhstan (Wikipedia Commons)
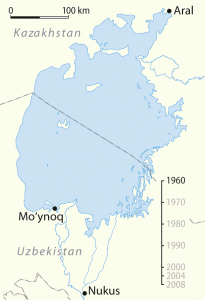 Moving map showing the shrinkage of the Aral Sea (Wikipedia Commons)
Moving map showing the shrinkage of the Aral Sea (Wikipedia Commons)
Video:
The “Nature” of Communism
A key aspect of the Soviet Union’s quest for true Communism was becoming waste-free and efficient. Every single resource was utilized for the common good of the state; this included people, materials, machines, and even nature. Unused land was waste, and waste had no place in the Party’s strategy.
Looking back, particularly with today’s heightened emphasis on preserving the environment, it is easy to see the ways in which these policies of brutal extraction from the land would lead to future consequences. The desiccation of the Aral Sea has not only caused serious environmental repercussions, but has also been linked to an increase in medical problems, such as cancer.
I was reading the excerpt on the Aral Sea thinking, “whew, so glad we know better now,” when I realized that thought was dead-wrong. We don’t really know any better. And the biggest environmental offender today? China, the other communist powerhouse from the 20th Century. Chinese cities have some of the worst air and water pollution ratings in the entire world, yet when it was approached with the Kyoto Protocol, which would require it to curb its actions that are so detrimental to the environment, it refused. China’s reasoning was that it was still a “developing nation” and shouldn’t be subjected to such environmental restraints—restraints that other, now-developed nations did not have to adhere to on their path to modernity. Russia would be one such example.
When using this China-parallel it would be easy to conclude that destroying the environment to the states’ benefit is a common facet among Communist states. I’m not sure I can soundly make that assertion, but I don’t think it is a coincidence that the two largest Communist (or near-Communist) countries have committed some of the worst atrocities towards the environment.
First Part of Project
Link
This is a section of my final project. It discusses the unseen consequences of the nuclear meltdown of Chernobyl with emphasis on the groundwater, wildlife, environment, and human death tolls.
Unintended Consequences of Nuclear Development
During my research for informational websites relevant to my topic, I came across a lot of overlapping information about the effects the nuclear industry has had on our environment. The two most valuable web sources are wikipedia, and the information from the nuclear weapons archive. Both websites have the most expansive but simultaneously in depth information on my topic. A few of the websites cover both high and low level effects on the environment, and others discuss the effects on humans and cancer on the subatomic level.
The websites span from topic of nuclear weapons testing to information justifying the banning of nuclear testing through the passing of treaties. My sources are all very recent with the exception of the source belonging to the nuclear weapons archive, which dates back to 1997. I did not use the Evernote application in my research, therefore I have no feedback to how it positively or negatively effected my progress. This is the first time I have ever used the Dropbox program. I found it to be very a straightforward and convenient way to share documents. The scope of my research hasn’t changed as a result of my new sources, as they all had specific relevance to my original topic. I am going to proceed by collaborating with Barret to make sure our research aligns to stay relevant, and will continue to focus on the unintended nuclear effects that testing and reactors have had on the environment and humans.
Shrinkage of the Aral Sea
My final report is about the shrinkage of the Aral Sea. I will be concentrating on four points. The first point is the cause of the shrinkage of the Aral Sea. I will discuss how the Soviets in Moscow wanted to harvest great quantities of cotton from Central Asia. In order to do this, they used the Aral Sea for irrigation to such an extent that the sea’s area shrank by 44%. This caused many health and environmental consequences for Central Asia.
The environmental consequences that I will discuss include flooding due to poor drainage systems, the poisoning of water and soil by pesticides used to grow the cotton, dust storms, and deforestation. The health consequences I plan on discussing include starvation, infant mortality, contaminated breast milk, and the prevalence of water-born illnesses such as typhoid, hepatitis, and dysentery.
The final point of discussion will be the possibility of rebuilding the Aral Sea, along with the successes that have occurred since the collapse of the USSR.
I will need to continue doing more research for my report. I am anticipating that the most challenging part of the project for me will not be the material, but the technological aspect of creating a website. This is the part that I will need to dedicate the most time to, as I have never done anything like it before.
So far, I have learned the importance of examining sources on multiple levels. First, getting articles from reliable databases, such as JSTOR, helps. Also, the fact that some of the authors I cited were cited in other scholarly articles gives more credibility to the authors. It is also important to have articles written by professionals, such as historians and scientists, and not university students or bloggers. The author’s credentials separate a scholarly article from an unscholarly article.
I also had to make sure, especially in the scientific texts, that I understood the point of the article. If an article is too difficult to comprehend, then it is pointless to cite it.
As for my critique of Evernote, my only issue was that it changed the format of the bibliography. I found it easier to use Microsoft Word.
Here is my annotated bibliography:
Bibliography
Josephson, Paul, R. Red Atom: Russia’s Nuclear Power Program from Stalin to Today. New York, NY: W.H. Freeman, 2000.
Red Atom discusses how political and cultural ideologies shaped the rapid development of the Soviet Union’s nuclear power program and the drawbacks which it faced. The leading advocates of nuclear proliferation were central planners that had been schooled in the Stalin era, yet manifested an acute awareness of that period’s disasters. Josephson extends his analysis of the origins of the Soviet nuclear program to the current status of Russia’s nuclear state. He concludes that fusing a determinist ideology with an unknown, potentially hazardous energy source can produce catastrophic results for the culture, politics, and environment. Red Atom: Russia’s Nuclear Power Program from Stalin to Today is a relevant source because it explains both the original intentions and the unintended past and future consequences of Russia’s nuclear program.
Park, Chris C. Chernobyl: The Long Shadow. London; New York: Routledge, 1989.
Chernobyl: The Long Shadow discusses the disastrous environmental effects of the Chernobyl nuclear meltdown in 1986. Park discusses the long term impact the nuclear fallout has had on humans and the environment. Park explains the important lessons learned by the scientific and public policy community from Chernobyl on managing nuclear sites and disasters. This information is imperative when researching the topic of unintended repercussions from harnessing nuclear energy as it discusses health and radiation, nuclear containment, and human issues. This book offers an opportunity to assess historiographical debates regarding Chernobyl, through comparison with The Chernobyl Accident: A Comprehensive Risk Assessment. Both cover the backlash from the same incident, giving me an opportunity to better understand potential overlap or disagreements within the scholarship.
Poyarkov, Victor. The Chernobyl Accident: A Comprehensive Risk Assessment. Edited by George J. Vargo. Columbus, OH: Battelle Press, 2000.
The book revolves around the global environmental fallout that was the product of the Chernobyl nuclear accident. The goal of this book is to uncover the actual environmental drawbacks from the nuclear meltdown, and to dispel false common public preconceptions about environmental catastrophe. What is concluded in this book is that the best way to approach this accident is to carefully study the effects that Chernobyl had so we can advance our knowledge with dealing with nuclear waste and radiation protection. There are eight original authors, all of whom are Russian and Ukrainian scientists that had first-hand work experience at the Chernobyl power plant before the explosion. I would be more skeptical of potential bias if it had not been for the later publishing date of 2000. This will be a great book for my research project because the authors have personal experience of actually being a Chernobyl scientist, which is invaluable. This source will be valuable to have to compare it to my other sources which focus on nuclear power plant management and sources involving Chernobyl.
Mousseau, Timothy A. and Anders P. Møller. “Landscape Portrait: A Look at the Impacts of Radioactive Contaminants on Chernobyl’s Wildlife.” Bulletin of the Atomic Scientists 67, no. 2 (2011): 38-46. Link
The purpose of this article was to address the popular misconception that the Chernobyl disaster had a smaller impact on the surrounding wildlife than it had on humans. The study found that there was a significant decrease in the reproductive habits of birds, a general decline of their overall health, and higher mutation rates than normal in the region of the Chernobyl site. The study was conducted by collecting sperm samples and analyzing them. This article will be helpful to my study because it offers a different aspect of environmental impact than my other sources–wildlife. For the environmental element of my paper, it will be important to try and draw connections to the Rogachevskaya article which also focuses on nuclear environmental issues.
Rogachevskaya, Liliya M. “Issues of Radioactivity and Sustainable Development Within Urban Groundwater Systems in Russia.” NATO Science Series. Series IV, Earth and Environmental Sciences 74. (2006): 251-257 Link
This article focuses on the contamination levels of the underground water supply in Russia since the dawn of the Soviet nuclear industry in the 1950s. The author claims that while the levels of radiation in the Russian water system are existent, they are not at levels associated with having detrimental effects on human health. She concludes that economic and social factors have more of a significant health impact in terms of contaminated water. This article is important to my research because it provides insight on what scientists and engineers should be focusing on to maintain nuclear sustainability, and how water contamination is not a source of major health concern. I am unaware of any potential biases the author would have in this area of study.
Scheblanov, VY, MK Sneve, and AF Bobrov. “Monitoring Human Factor Risk Characteristics at Nuclear Legacy Sites in Northwest Russia in Support of Radiation Safety Regulation.” Journal of Radiological Protection 32, no. 4 (2012): 465-477. Link
This article explains how the Norwegian government and the Russian Federal Medical–Biological Agency are advocating for better protection for workers from remnants of radiation from nuclear waste in nuclear storage sites. The article discusses the importance of advancements in techniques workers use to store hazardous nuclear waste as a factor in promoting worker safety. Additionally, the article offers suggestions on how to reduce potential factors which leave workers more vulnerable to radiation poisoning by quantifying human risk, and consistently monitoring human psychological health. This article will be very useful to my research as it is imperative to understand how to safely and properly dispose of nuclear waste in order to make it a sustainable source of energy. One important component of this article was that it was written in 2012. What do we know about the authors?
Stulberg , Adam N., Vladimir A. Orlov, and James Clay Moltz. Preventing Nuclear Meltdown: Managing Decentralization of Russia’s Nuclear Complex. Ashgate, 2004.
The central focus of this book is a deeper look into the security strategies which the Russian federal agencies had to implement in order to safeguard Russia’s nuclear complexes in both military, but especially civilian contexts. This book illuminates the wary steps that federal agencies took to prevent nuclear disaster. Moltz, Orlov, and Stulberg present valuable material which gives the reader a rare look at civilian criminology in relation to nuclear power plants. The book covers the different security strategies used from region to region. This book is valuable for my research project because it presents a connection to the nuclear industry to civilian life that my other sources do not, while still maintaining relevance to my research topic of being about the unintended consequences of Russian nuclear development. Both Scheblanov’s article and Stulberg’s article probe the inner workings of security in nuclear power plant sites but land on different focal points. It will be valuable to combine these two different elements of inner and outer security dilemmas.
Annotated Bibliography
Here is my annotated bibliography.